CELLYTPN1
CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit
For plant leaves
Synonyme(s) :
Cell lysis kit
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Code UNSPSC :
41116134
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.56
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Utilisation
kit sufficient for 30 extractions (20 g of fresh or frozen leaves)
Technique(s)
ChIP: suitable
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Description générale
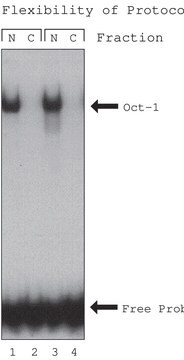
CelLytic™-PN extraction kit is for the isolation of nuclei and extraction of functional nuclear proteins from plant leaves. Nuclei or nuclear proteins can be extracted from few grams to hundreds grams of fresh and frozen leaves. The nuclear protein extract is suitable for the detection of DNA-protein interactions using gel-shift assay, DNase-I footprinting analysis as well as western blot assay and similar techniques. The isolated nuclei can also be used as a source for chromatin, genomic DNA and histones.
Application
The nuclear protein extract is suitable for the detection of DNA-protein interactions using gel-shift assay, DNase-I footprinting analysis as well as Western blot assay and similar techniques. The isolated nuclei can also be used as a source for chromatin, genomic DNA, RNA, etc. The kit provides a detailed protocol for nuclei isolation and protein extraction from four plant models: tobacco, tomato, spinach, and Arabidopsis.
Caractéristiques et avantages
Efficient Nuclei Isolation and Protein Extraction: CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit provides a fast and efficient method for isolating nuclei and extracting functional nuclear proteins from plant leaves, saving time and effort for academic researchers.
Versatility: The isolated nuclei can be used as a source for chromatin, genomic DNA, RNA, etc., making CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit a versatile solution for plant molecular biology research.
Suitable for Detection of DNA-Protein Interactions: The nuclear protein extract obtained using this kit is ideal for detecting DNA-protein interactions using gel-shift assay, DNase-I footprinting analysis, western blot assay, and similar techniques, which is crucial for researchers studying transcription factors and chromatin remodeling.
Plant Model Specific Protocol: The CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit offers a detailed protocol for nuclei isolation and protein extraction from four plant models: tobacco, tomato, spinach, and Arabidopsis, making it an easy-to-follow solution for researchers working with these plant models.
Rapid Extraction: The CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit provides academic researchers with a rapid extraction method, allowing them to quickly extract functional nuclear proteins from plant leaves for their research.
Versatility: The isolated nuclei can be used as a source for chromatin, genomic DNA, RNA, etc., making CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit a versatile solution for plant molecular biology research.
Suitable for Detection of DNA-Protein Interactions: The nuclear protein extract obtained using this kit is ideal for detecting DNA-protein interactions using gel-shift assay, DNase-I footprinting analysis, western blot assay, and similar techniques, which is crucial for researchers studying transcription factors and chromatin remodeling.
Plant Model Specific Protocol: The CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit offers a detailed protocol for nuclei isolation and protein extraction from four plant models: tobacco, tomato, spinach, and Arabidopsis, making it an easy-to-follow solution for researchers working with these plant models.
Rapid Extraction: The CelLytic™ PN Isolation/Extraction Kit provides academic researchers with a rapid extraction method, allowing them to quickly extract functional nuclear proteins from plant leaves for their research.
Autres remarques
This kit is for the rapid isolation of nuclei and extraction of functional nuclear proteins from plant leaves. Nuclei or nuclear proteins can be extracted from a few grams to hundreds of grams of fresh and frozen leaves.
Informations légales
CelLytic is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Réf. du produit
Description
Tarif
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Xiaosa Xu et al.
Developmental cell, 56(4), 557-568 (2021-01-06)
Crop productivity depends on activity of meristems that produce optimized plant architectures, including that of the maize ear. A comprehensive understanding of development requires insight into the full diversity of cell types and developmental domains and the gene networks required
Rwitie Mallik et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta. Gene regulatory mechanisms, 1863(12), 194644-194644 (2020-10-18)
AtHMGB15 belongs to a group of ARID-HMG proteins which are plant specific. The presence of two known DNA binding domains: AT rich interacting domain (ARID) and High Mobility Group (HMG)-box, in one polypeptide, makes this protein intriguing. Although proteins containing
Jonguk An et al.
Frontiers in plant science, 12, 672552-672552 (2021-06-08)
Flavonoids are well known for the coloration of plant organs to protect UV and ROS and to attract pollinators as well. Flavonoids also play roles in many aspects of physiological processes including pathogen resistance. However, the molecular mechanism to explain
Bo Lv et al.
Journal of cell science, 130(9), 1662-1674 (2017-03-18)
Cilia are microtubule-based organelles and perform motile, sensing and signaling functions. The assembly and maintenance of cilia depend on intraflagellar transport (IFT). Besides ciliary localization, most IFT proteins accumulate at basal bodies. However, little is known about the molecular mechanism
Andrew Farmer et al.
Molecular plant, 14(3), 372-383 (2021-01-11)
Similar to other complex organisms, plants consist of diverse and specialized cell types. The gain of unique biological functions of these different cell types is the consequence of the establishment of cell-type-specific transcriptional programs. As a necessary step in gaining
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique