CE0050
CelLytic™ MEM Protein Extraction Kit
Synonyme(s) :
Membrane protein extraction kit
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Code UNSPSC :
41116134
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.56
Produits recommandés
Technique(s)
protein extraction: suitable
Niveau de qualité
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
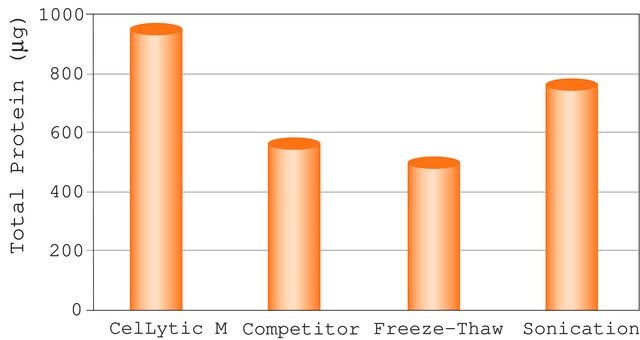
CelLytic™ MEM Protein Extraction Kit offers a fast and convenient method to isolate hydrophobic and raft microdomain associated proteins from cells. The method is based on phase separation and does not require cell membrane isolation. The separated proteins can be used for further experiments such as SDS-PAGE, Western blotting, dot blotting, and immunoprecipitation. The kit has been tested on, but not limited to, HeLa, HEK-293, NIH 3T3, COS and CHO cell lines.
Membrane proteins make up around 20-30% of an organism′s genome and serve as cellular gatekeepers, regulators, and sensors. They have diverse cellular functions, such as shielding the cell from external toxins, being the starting point of intracellular signaling cascades, and retaining critical ion concentrations.
Application
CelLytic™ MEM Protein Extraction Kit has been used for de novo lipogenesis measurements using hepatocytes and to extract membrane proteins for western blotting.
Adéquation
Sufficient reagents supplied for 80 tests.
Informations légales
CelLytic is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Composants de kit seuls
Réf. du produit
Description
- Lysis and Separation Buffer 50 mL
- Wash Buffer for CelLytic MEM 50 mL
- Sodium Chloride, 4M Solution 1.5 mL
Composants de kit également disponibles séparément
Réf. du produit
Description
FDS
- P8340Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, for use with mammalian cell and tissue extracts, DMSO solution 1 mLFDS
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Point d'éclair (°F)
188.6 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
87 °C - closed cup
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Elisabeth P Carpenter et al.
Current opinion in structural biology, 18(5), 581-586 (2008-08-05)
Membrane protein structural biology is still a largely unconquered area, given that approximately 25% of all proteins are membrane proteins and yet less than 150 unique structures are available. Membrane proteins have proven to be difficult to study owing to
Tomoaki Furuta et al.
Cancer science, 112(9), 3722-3731 (2021-06-12)
The rBC2LCN lectin, known as a stem cell marker probe that binds to an H type 3 fucosylated trisaccharide motif, was recently revealed to also bind to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells. A lectin-drug conjugate was generated by fusing rBC2LCN
Willy Morelle et al.
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 102(4), 1375-1386 (2017-03-23)
TMEM165 deficiency is a severe multisystem disease that manifests with metabolic, endocrine, and skeletal involvement. It leads to one type of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG), a rapidly growing group of inherited diseases in which the glycosylation process is altered.
Yue Zhao et al.
Cancer medicine, 7(8), 3977-3987 (2018-07-06)
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a malignant disease with poor prognosis. Because of early metastasis prior to diagnosis and therapeutic resistance, ESCC has become one of the leading causes of cancer-related death. Here, we investigated the clinicopathological significance of
Emily C Cokorinos et al.
Cell metabolism, 25(5), 1147-1159 (2017-05-04)
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a potential therapeutic target for metabolic diseases based on its reported actions in the liver and skeletal muscle. We evaluated two distinct direct activators of AMPK: a non-selective activator of all AMPK complexes, PF-739
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique