A7236
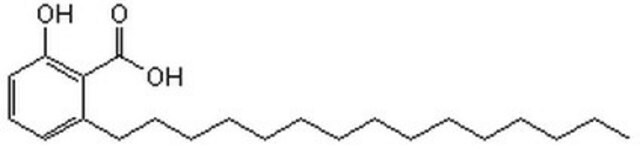
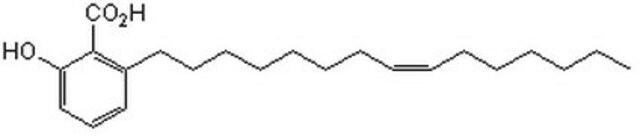
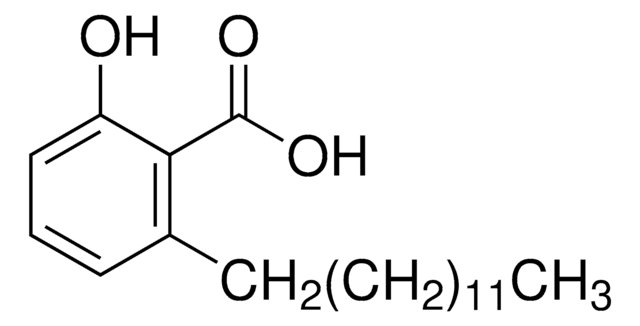
Anacardic acid
Synonyme(s) :
2-Hydroxy-6-pentadecylbenzoic acid, 22:0-Anacardic acid, 6-Pentadecylsalicylic acid
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
powder
Niveau de qualité
Conditions de stockage
protect from light
Couleur
white to beige
Solubilité
DMSO: ≥20 mg/mL
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCc1cccc(O)c1C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C22H36O3/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-16-19-17-15-18-20(23)21(19)22(24)25/h15,17-18,23H,2-14,16H2,1H3,(H,24,25)
Clé InChI
ADFWQBGTDJIESE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Application
- as a histone acetylase (HAT) inhibitor to study its effects on rat cortical neurons
- as a positive control in acetylation assay in vitro
- as an acetylase inhibitor to study its effects on the ribonucleic acid export 1 (Rae-1) protein acetylation that was transfected in human embryonic kidney cells
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Caractéristiques et avantages
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Epigenetic modifications are thought to occur through two key interconnected processes—DNA methylation and the covalent modification of histones.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique