A4268
α-Amylase from porcine pancreas
Type I-A, PMSF treated, saline suspension, 700-1400 units/mg protein (E1%/280)
Synonyme(s) :
β-N-acetylglucosaminidase porcine placenta, PPA, al1,4 glucan-4-glucanohydrolase,, porcine pancreas α-amylase
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
Porcine pancreas
Type
Type I-A
Forme
saline suspension
Activité spécifique
700-1400 units/mg protein (E1%/280)
Poids mol.
51-54 kDa
Caractéristiques du produit alternatif plus écologique
Waste Prevention
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
Adéquation
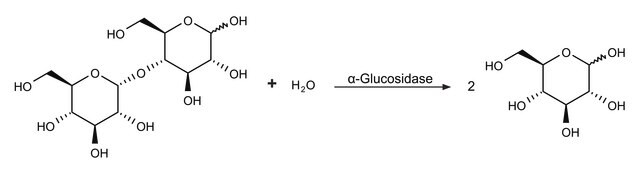
suitable for hydrolysis, synthesis of oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, and sugar modification
Application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
Autre catégorie plus écologique
, Enabling
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
α-Amylase isolated from porcine pancreas is a glycoprotein. It is a single polypeptide chain of ~475 residues containing two SH groups and four disulfide bridges and a tightly bound Ca2+ necessary for stability. Chloride ions are necessary for activity and stability. The pH range for activity is 5.5 to 8.0, with the pH optimum at 7.
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Définition de l'unité
Forme physique
Notes préparatoires
Autres remarques
Inhibiteur
Substrat
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique