42395
Tannase from Aspergillus ficuum
powder, white, ≥150 U/g
Synonyme(s) :
Tannin acyl Hydrolase
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Numéro CAS:
Numéro CE :
Numéro MDL:
Code UNSPSC :
12352204
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.54
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
Aspergillus sp. (A. ficuum)
Niveau de qualité
Forme
powder
Activité spécifique
≥150 U/g
Impuretés
25 mM potassium phosphate
250 mM NaCl
50% glycerol
Couleur
white
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Description générale
Tannase is an enzyme that is produced by several organisms such as plants, bacteria, fungi, and yeast. This enzyme is also found in plant sources such as tannin-rich vegetables, especially in the leaves, fruits, branches, and bark.
Application
Tannase from Aspergillus ficuum has been used:
- as a standard to determine the tannase activity of bacterial isolates
- to study its effects on the inhibitory activity of tannic acid on biofilm formation
- to obtain Proanthocyanidins (PA) by enzymatic hydrolysis of grape skin and seeds
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
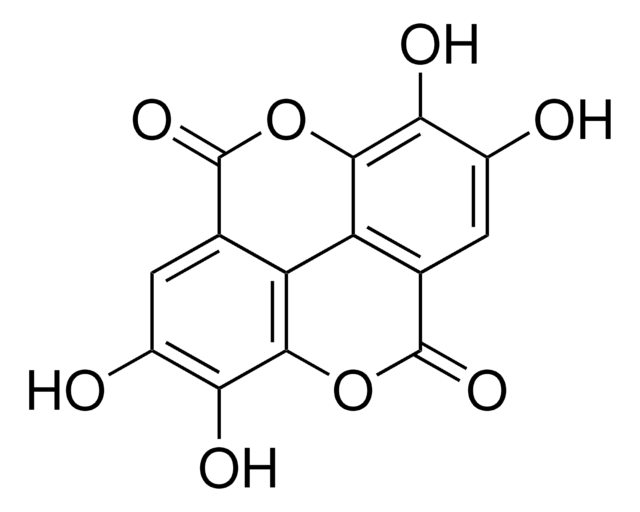
Tannase catalyzes the ester bonds located in complex tannins, gallo-tannins, and gallic acid esters, which results in the release of gallic acid. This enzyme can be used as a clarifying agent in the manufacture of beer, tea, wine, and juices and to treat tannin-polluting agricultural waste and industrial effluents.
Définition de l'unité
1 U corresponds to the amount of enzyme which changes the absorbance at 310 nm by 1.0 per minute at pH 4.7 and 30°C (tannic acid as substrate, final volume 3 ml)
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Arijit Jana et al.
Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 167(5), 1254-1269 (2012-01-25)
Tannase production by newly isolated Penicillium purpurogenum PAF6 was investigated by 'one variable at a time' (OVAT) approach followed by response surface methodology (RSM). Tannin-rich plant residues were used as supporting solid substrate and sole carbon source and, among them
Jose Valdo Madeira et al.
Bioprocess and biosystems engineering, 35(3), 477-482 (2011-09-13)
The production of enzymes such as tannases and phytases by solid-state fermentation and their use in animal feed have become a subject of great interest. In the present work, Paecilomyces variotii was used to produce tannase and phytase simultaneously. Solid-state
Jose Valdo Madeira et al.
Bioresource technology, 102(15), 7343-7348 (2011-05-27)
In this work, we introduce a biological detoxification method that converts toxic waste from castor beans into animal feed material. This method simultaneously induces the production of tannase and phytase by Paecilomyces variotii; both enzymes have high levels of activity
Bhakti Bajpai et al.
Brazilian journal of microbiology : [publication of the Brazilian Society for Microbiology], 39(4), 708-711 (2008-10-01)
In a new approach to microbial gallic acid production by Aspergillus fischeri MTCC 150, 40gL(-1) of tannic acid was added in two installments during the bioconversion phase of the process (25gL(-1) and 15gL(-1) at 32 and 44h respectively). The optimum
Tadashi Takahashi et al.
Eukaryotic cell, 11(4), 507-517 (2012-01-31)
Loop-out-type recombination is a type of intrachromosomal recombination followed by the excision of a chromosomal region. The detailed mechanism underlying this recombination and the genes involved in loop-out recombination remain unknown. In the present study, we investigated the functions of
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique