776130
3-Azido-1-propanol
≥96%
Synonyme(s) :
1-Azidopropan-3-ol
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Formule empirique (notation de Hill) :
C3H7N3O
Numéro CAS:
Poids moléculaire :
101.11
Numéro MDL:
Code UNSPSC :
12352125
ID de substance PubChem :
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.22
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥96%
Forme
liquid
Capacité de réaction
reaction type: click chemistry
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.461
Densité
1.095 g/mL at 25 °C
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Chaîne SMILES
OCCCN=[N+]=[N-]
InChI
1S/C3H7N3O/c4-6-5-2-1-3-7/h7H,1-3H2
Clé InChI
WHVSIWLMCCGHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
3-Azido-1-propanol is an azide-containing reagent utilized in Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition reactions (SPAAC). This enables selective and copper-free click chemistry modifications of biomolecules.
Application
3-Azido-1-propanol is used as a:
- Precursor in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds like dihydrooxazines
- Reagent in the synthesis of heterofunctional polyesters by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
1, 3-Dipolar and Diels-Alder cycloaddition reactions on polyester backbones possessing internal electron-deficient alkyne moieties
M Cetin, et.al.
Polym. Chem., 7, 7094-7100 (2016)
Efficient synthesis of linear multifunctional poly (ethylene glycol) by copper (I)-catalyzed Huisgen 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition
Liu X-M, et al.
Biomacromolecules, 8(9), 2653-2658 (2007)
1, 3-Dipolar and Diels-Alder cycloaddition reactions on polyester backbones possessing internal electron-deficient alkyne moieties
Cetin M, et al.
Polym. Chem., 7(46), 7094-7100 (2016)
Cross-linked polymer-blend gate dielectrics through thermal click chemistry
Li S, et al.
Chemistry?A European Journal, 21(49), 17762-17768 (2015)
Somayeh Khezrian et al.
Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 108(11), 2291-2304 (2020-05-05)
Active targeted nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems have gained significant favor because they have the ability to decrease side effects, improve drug bioavailability, and the potency of anticancer treatment. In this study, functional amphiphilic Janus nanoparticles (JNPs), consisting of hydrophilic and
Global Trade Item Number
| Référence | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 776130-1G | 4061826736333 |
| 776130-5G | 4061833332627 |
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique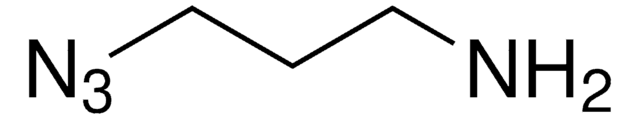
![2-[2-(2-Azidoethoxy)ethoxy]ethanol solution ~0.5 M in tert-butyl methyl ether](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/374/007/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a/640/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a.png)