Alle Fotos(1)
Wichtige Dokumente
P3243
Phosphodiesterase I aus Crotalus adamanteus Gift
vial of ≥100 units, Purified
Synonym(e):
5′-Exonuclease, Oligonucleat-5′-Nucleotidohydrolase
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Biologische Quelle
Crotalus adamanteus venom
Qualitätsniveau
Form
solid
Qualität
Purified
Spezifische Aktivität
≥20.0 unit/mg solid
Verpackung
vial of ≥100 units
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
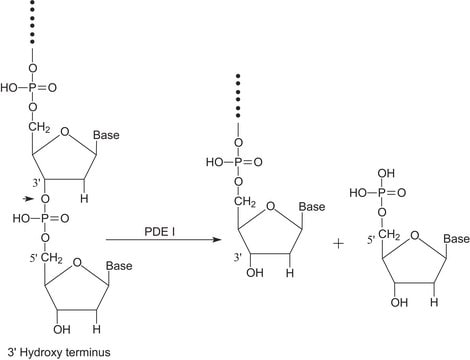
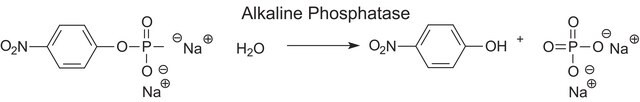
Jedes Enzym, das zum Aufbrechen von Phosphodiesterbindungen verwendet wird, ist eine Phosphodiesterase (PDE). Es ist ein membrangebundenes Glykoprotein, das zur Katalyse der Hydrolyse verschiedener Nukleotid-Polyphosphate eingesetzt wird. Phosphodiesterase I wird in Phosphodiesterase-Aktivierungstests zur Hydrolyse von AMP verwendet. Das Produkt P3243 stammt aus dem Gift des Crotalus adamanteus und ist aufgereinigt. Das Produkt P3243 wird zur Hydrolyse von tRNA mit Wyosinderivaten zu Mononukleosiden verwendet.
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Phosphodiesterase I bricht Phosphodiesterbindungen auf und katalysiert die Hydrolyse verschiedener Nukleotidpolyphosphate. Phosphodiesterase I wird aus eukaryotischen Plasmamembranen durch phosphatidylinositolspezifische Phospholipase C freigesetzt.
Einheitendefinition
Eine Einheit hydrolysiert ein μMol p-Nitrophenyl-Thymidin-5-Phosphat pro Minute bei 25 °C, pH 8,9
Angaben zur Herstellung
Aufgereinigt mit der Methode von Williams et al. und weiterbehandelt, um die kontaminierende 5′-Nukleotidase-Aktivität zu inaktivieren.
Rekonstituierung
Zu Prüfzwecken wird PDE I in kaltem demineralisiertem Wasser mit 0,1–0,2 E/ml rekonstituiert.
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
P-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Resp. Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Action of venom phosphodiesterase on deoxyribonucleic acid.
E J WILLIAMS et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 236, 1130-1134 (1961-04-01)
Valérie de Crécy-Lagard et al.
Molecular biology and evolution, 27(9), 2062-2077 (2010-04-13)
Wyosine (imG) and its derivatives such as wybutosine (yW) are found at position 37 of phenylalanine-specific transfer RNA (tRNA(Phe)), 3' adjacent to the anticodon in Eucarya and Archaea. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, formation of yW requires five enzymes acting in a
Alain R Weber et al.
Nature communications, 7, 10806-10806 (2016-03-05)
Cytosine methylation in CpG dinucleotides is an epigenetic DNA modification dynamically established and maintained by DNA methyltransferases and demethylases. Molecular mechanisms of active DNA demethylation began to surface only recently with the discovery of the 5-methylcytosine (5mC)-directed hydroxylase and base
N Shenoy et al.
Blood cancer journal, 7(7), e587-e587 (2017-07-22)
The Ten Eleven Translocation (TET) enzymes have been found to be mutated in both diffuse large B-cell (DLBCL) and peripheral T-cell (PTCL) lymphomas resulting in DNA hypermethylation. Recent studies in embryonal stem cells showed that ascorbic acid (AA) is a
Yana Konokhova et al.
Skeletal muscle, 6, 10-10 (2016-02-20)
Low mitochondrial content and oxidative capacity are well-established features of locomotor muscle dysfunction, a prevalent and debilitating systemic occurrence in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although the exact cause is not firmly established, physical inactivity and oxidative stress
Protokolle
Enzymatic Assay of 5’-Nucleotidase
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.