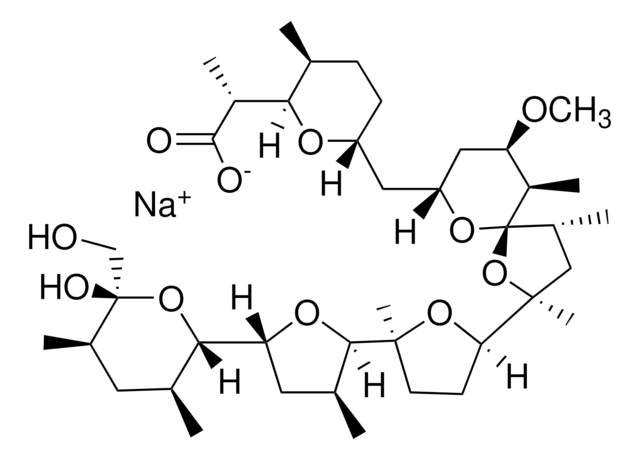
481990
Nigericin, Sodium Salt, Streptomyces hygroscopicus
Disrupts the membrane potential and stimulates ATPase activity in mitochondria.
Synonym(e):
Nigericin, Sodium Salt, Streptomyces hygroscopicus, Antibiotic K178
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥98% (TLC)
Form
lyophilized
Hersteller/Markenname
Calbiochem®
Lagerbedingungen
OK to freeze
Löslichkeit
chloroform: soluble
ethanol: soluble
ethyl acetate: soluble
Versandbedingung
ambient
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C40H68O11.Na/c1-21-11-12-28(46-33(21)26(6)36(42)43)17-29-18-30(45-10)27(7)40(48-29)25(5)19-38(9,51-40)32-13-14-37(8,49-32)35-23(3)16-31(47-35)34-22(2)15-24(4)39(44,20-41)50-34;/h21-35,41,44H,11-20H2,1-10H3,(H,42,43);/q;+1/p-1/t21-,22-,23-,24+,25?,26?,27+,28+,29+,30+,31+,32?,33?,34-,35?,37?,38?,39-,40+;/m0./s1
InChIKey
MOYOTUKECQMGHE-KKCUGXASSA-M
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Disrupts the membrane potential and stimulates ATPase activity in mitochondria.
Warnhinweis
Rekonstituierung
Sonstige Hinweise
Eytan, G.D., et al. 1990. J. Biol. Chem.265, 12949.
Alonso, M.A., and Carrasco, L. 1981. FEBS Lett.127, 112.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.