Wichtige Dokumente
81323
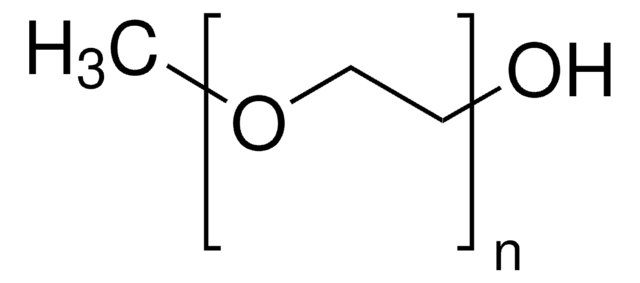
Poly(ethylenglycol)methylether
average MN 5,000, methoxy, hydroxyl
Synonym(e):
Methoxy-polyethylenglykol, Polyethylenglykol-monomethylether, mPEG
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
product name
Poly(ethylenglycol)methylether, average Mn 5,000
Dampfdichte
>1 (vs air)
Qualitätsniveau
Dampfdruck
0.05 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Form
flakes
powder or crystals
Mol-Gew.
average Mn 5,000
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
60-64 °C
Ω-Ende
hydroxyl
α-Ende
methoxy
InChI
1S/C3H8O2/c1-5-3-2-4/h4H,2-3H2,1H3
InChIKey
XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Anwendung
Sonstige Hinweise
Ähnliches Produkt
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
359.6 °F - closed cup
Flammpunkt (°C)
182 °C - closed cup
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Die passende Version wird nicht angezeigt?
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Version benötigen, können Sie anhand der Lot- oder Chargennummer nach einem spezifischen Zertifikat suchen.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Artikel
Fouling Resistant Biomimetic Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Based Grafted Polymer Coatings
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.