GS66
GST M2-2, Recombinant Human
Sinônimo(s):
GST4, GSTM, GTHMUS, glutathione S-transferase mu 2
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.26
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
human
Nível de qualidade
recombinante
expressed in E. coli
Ensaio
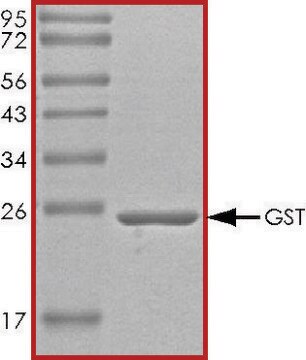
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
forma
frozen liquid
atividade específica
93.3 units/mg protein
peso molecular
26 kDa
concentração
2.55 mg/mL
temperatura de armazenamento
−70°C
Informações sobre genes
human ... GSTM2(2946)
Descrição geral
using spectrophotometric determination of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) conjugation with reduced glutathione (1 mM) in 100 mM NaPO4 (pH 6.5) at room temperature.
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Glutathione S-transferase mu 2 (GSTM2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSTM2 gene. Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are a family of enzymes that play an important role in detoxification by catalyzing the conjugation of many hydrophobic and electrophilic compounds with reduced glutathione. Based on their biochemical, immunologic, and structural properties, cytosolic and membrane-bound forms of glutathione S-transferase are encoded by two distinct supergene families. At present, eight distinct classes of the soluble cytoplasmic mammalian glutathione S-transferases have been identified: alpha, kappa, mu, omega, pi, sigma, theta and zeta. The GSTs are thought to function in xenobiotic metabolism and play a role in susceptibility to cancer, and other diseases.
This gene encodes a glutathione S-transferase that belongs to the mu class. The mu class of enzymes functions in the detoxification of electrophilic compounds, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins and products of oxidative stress, by conjugation with glutathione. The genes encoding the mu class of enzymes are organized in a gene cluster on chromosome 1p13.3 and are known to be highly polymorphic. These genetic variations can change an individual′s susceptibility to carcinogens and toxins as well as affect the toxicity and efficacy of certain drugs.
Armazenamento e estabilidade
The enzyme should be used by the end-user customer within 1 year of receipt.
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Ruwani Hewawasam et al.
Biochemical pharmacology, 80(3), 381-388 (2010-04-27)
Ca(2+) release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through cardiac ryanodine receptors (RyR2) is essential for heart function and is inhibited by the carboxy terminal domain of glutathione transferase M2-2 (GSTM2-C) and derivative fragments containing helix 6. Since a peptide encoding helix
Ihn Han et al.
Proteomics, 11(3), 352-360 (2011-01-27)
Ovarian teratoma is a dermoid cyst in the ovary that contains mature tissues such as hair, teeth, bone, thyroid, etc. To understand the molecular mechanisms of ovarian teratoma growth, a comparative proteomic analysis was undertaken using mesenchymal stem cell-like cells
Mao-Wen Weng et al.
DNA repair, 4(4), 493-502 (2005-02-24)
Cellular detoxification is important for the routine removal of environmental and dietary carcinogens. Glutathione S-transferases (GST) are major cellular phase II detoxification enzymes. MRC-5 cells have been found to exhibit significantly higher GST activity than human H1355 cells. This study
Lan Wei et al.
The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 40(8), 1616-1628 (2008-03-01)
We show that a glutathione transferase (GST) protein, which is recognised by an antibody against the muscle-specific human GSTM2-2 (hGSTM2-2), is associated with the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle. We further show
Ying-Hao Shen et al.
Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine, 35(5), 4007-4015 (2014-01-09)
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most serious health problems worldwide. As in many other diseases, environment and genetic factors are believed to be involved in the pathogenesis of HCC. Numerous epidemiologic investigations including case-control and cohort studies have
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica