725366
Iron oxide(II,III), magnetic nanoparticles solution
20 nm avg. part. size, 5 mg/mL in H2O
Sinônimo(s):
Magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals, Magnetite, Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Formulário
dispersion
nanoparticles
Nível de qualidade
concentração
5 mg/mL in H2O
magnetização
>20 emu/g, at 4500Oe
tamanho de partícula
18-22 nm
Tamanho médio da partícula
20 nm
densidade
1.00 g/mL at 25 °C
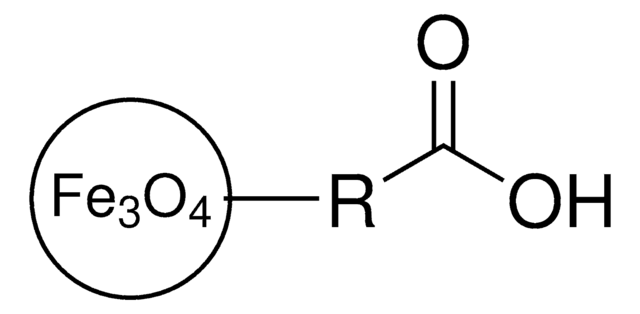
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O=[Fe].O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O
InChI
1S/3Fe.4O
chave InChI
SZVJSHCCFOBDDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (IONP) synthesis to applications: present and future: This report outlines the co-precipitation synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles using Fe(II) and Fe(III) solutions and discusses their future applications (N Ajinkya et al., 2020).
- Surface modification of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Explores the surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) to enhance their functionality for various applications (N Zhu et al., 2018).
- Recent advances on iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles as sorbents of organic pollutants in water and wastewater treatment: Discusses the use of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles in removing organic pollutants from water, highlighting the synthesis of core-shell magnetic nanoparticles (AM Gutierrez et al., 2017).
- Potential toxicity of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: Reviews the potential toxic effects of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles, emphasizing their stability, biocompatibility, and size control (N Malhotra et al., 2020).
- Co-precipitation in aqueous solution synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles using iron (III) salts as precursors: Details the synthesis process of iron oxide nanocrystals and their potential applications in various fields (MI Khalil, 2015).
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
nwg
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Currently, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are attracting a lot of attention because of the possibility of many novel applications, especially in biomedical research.
Professor Mitsuhiro Ebara provides insights on several types of smart nanofiber mesh systems that have been explored for different drug delivery purposes.
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
Professor Hui Mao explores the use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (INOPs) that offer an alternate contrast-enhancing mechanism.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 725366-5ML | 4061832861494 |
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica