409537
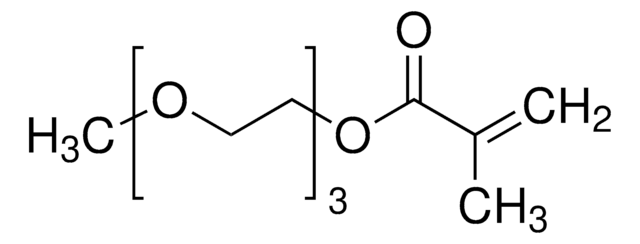
Poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate
average Mn 360, methacrylate, 500-800 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
Sinônimo(s):
Ethoxylated 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, PEGMA, Poly(ethylene oxide) monomethacrylate, Polyethylene glycol
About This Item
product name
Poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate, average Mn 360, contains 500-800 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
forma
liquid
peso molecular
average Mn 360
contém
500-800 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
adequação da reação
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
índice de refração
n20/D 1.464
densidade
1.105 g/mL at 25 °C
Ω-final
hydroxyl
α-final
methacrylate
arquitetura do polímero
shape: linear
functionality: heterobifunctional
InChI
1S/C6H10O3/c1-5(2)6(8)9-4-3-7/h7H,1,3-4H2,2H3
chave InChI
WOBHKFSMXKNTIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- Degradable microspheres using asuspension polymerization process. The amphiphilic nature of PEGMA allows performingthe polymerization by direct oil in the water suspension process.
- Polymeric chelating beads for the effectiveremoval of heavy metals from aqueous solutions.
forma física
Palavra indicadora
Warning
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Skin Irrit. 2
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica