SAE0093
Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1
B4GALT1 human recombinant, expressed in HEK 293 cells, 2000 units/mg protein
Synonyme(s) :
Beta-1,4-GalTase 1, Beta4Gal-T1, UDP-Gal:beta-GlcNAc beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1, UDP-galactose:beta-N-acetylglucosamine beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1, b4Gal-T1
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Produit recombinant
expressed in HEK 293 cells
Essai
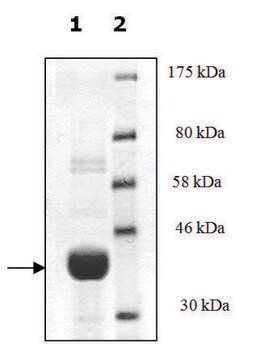
95% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
lyophilized powder
Activité spécifique
2000 units/mg protein
Conditions d'expédition
ambient
Température de stockage
−20°C
Description générale
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
A major function of B4GALT1 is the addition of β(1→4) linked galactose residues to oligosaccharide acceptors with terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues. This is a late elongation step in the N-glycan processing pathway.B4GALT1 enzymatic activity is widely distributed in the vertebrate kingdom, in both mammals and non-mammals, including avians and amphibians.B4GALT1 enzymatic activity has also been demonstrated in a subset of plants which diverged from animals an estimated 1 billion years ago.B4GALT1 interacts with α-lactalbumin (LA), a protein expressed in the mammary gland during lactation, to form the lactose synthase (LS) complex that transfers galactose from UDP-α-D-Gal to glucose, producing the lactose secreted in milk.Defects in B4GALT1 are the cause of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 2D (CDG2D).Glomerular B4GALT1 expression has been found to be increased in IgA nephropathy. IgA binding and IgA-induced mesangial cell phosphorylation of spleen tyrosine kinase and IL-6 synthesis were inhibited by a panel of β(1→4) galactosyltransferase-specific antibodies, which suggests that IgA binds to the catalytic domain of β(1→4) galactosyltransferase.
Définition de l'unité
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Glycosyltransferases were initially considered to be specific for a single glycosyl donor and acceptor, which led to the one enzyme-one linkage concept. Subsequent observations have refuted the theory of absolute enzymatic specificity by describing the transfer of analogs of some nucleoside mono- or diphosphate sugar donors.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique