380R-2
Arginase-1 (EP261) Rabbit Monoclonal Primary Antibody
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
rabbit
Niveau de qualité
100
500
Conjugué
unconjugated
Forme d'anticorps
culture supernatant
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
EP261, monoclonal
Description
For In Vitro Diagnostic Use in Select Regions
Forme
buffered aqueous solution
Espèces réactives
human
Conditionnement
vial of 0.1 mL concentrate (380R-24)
vial of 0.1 mL concentrate Research Use Only (380R-24-RUO)
vial of 0.5 mL concentrate (380R-25)
vial of 1.0 mL concentrate (380R-26)
vial of 1.0 mL concentrate Research Use Only (380R-26-RUO)
vial of 1.0 mL pre-dilute Research Use Only (380R-27-RUO)
vial of 1.0 mL pre-dilute ready-to-use (380R-27)
vial of 7.0 mL pre-dilute ready-to-use (380R-28)
vial of 7.0 mL pre-dilute ready-to-use Research Use Only (380R-28-RUO)
Fabricant/nom de marque
Cell Marque™
Technique(s)
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:50-1:200 (concentrated)
Isotype
IgG
Contrôle
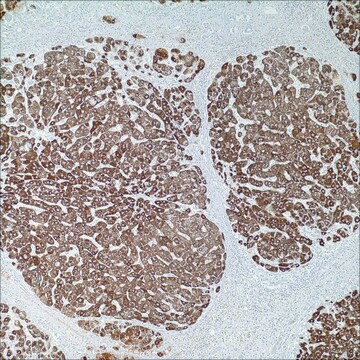
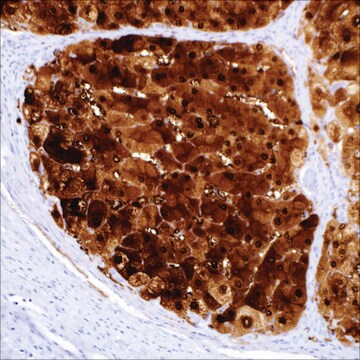
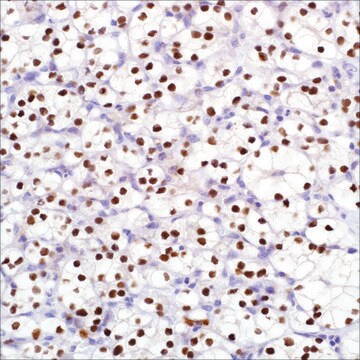
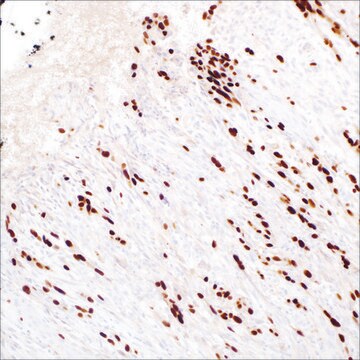
hepatocellular carcinoma, normal liver
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Visualisation
cytoplasmic, nuclear
Informations sur le gène
human ... ARG1(383)
Description générale
Qualité
 IVD |  IVD |  IVD |  RUO |
Liaison
Forme physique
Notes préparatoires
Note: This requires a keycode which can be found on your packaging or product label.
Download the latest released IFU
Note: This IFU may not apply to your specific product lot.
Autres remarques
Informations légales
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique