I0627
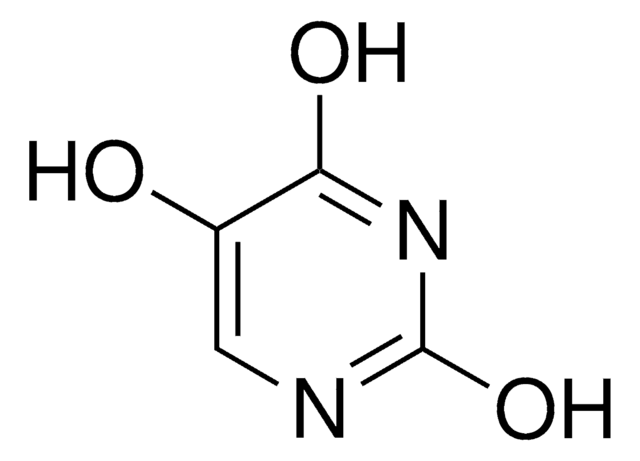
Isobarbituric acid
analytical standard
Synonyme(s) :
2,4,5-Trihydroxypyrimidine, 5-Hydroxyuracil
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
analytical standard
Niveau de qualité
Essai
~98%
Technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
Pf
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Application(s)
forensics and toxicology
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
veterinary
Format
neat
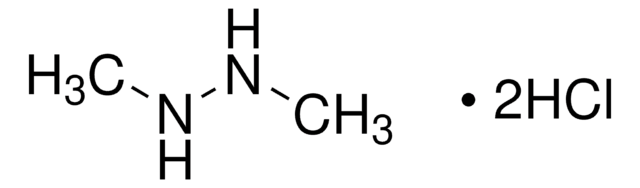
Chaîne SMILES
O=C1CNC(=O)NC1=O
InChI
1S/C4H4N2O3/c7-2-1-5-4(9)6-3(2)8/h1H2,(H2,5,6,8,9)
Clé InChI
FQXOOGHQVPKHPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Application
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique