764752
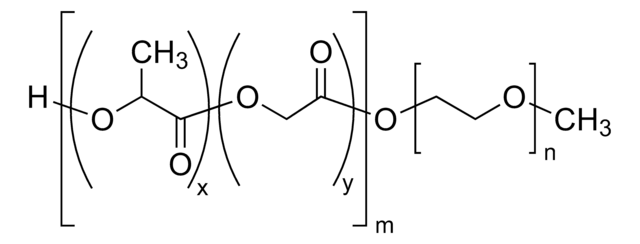
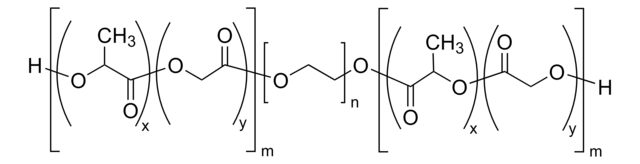
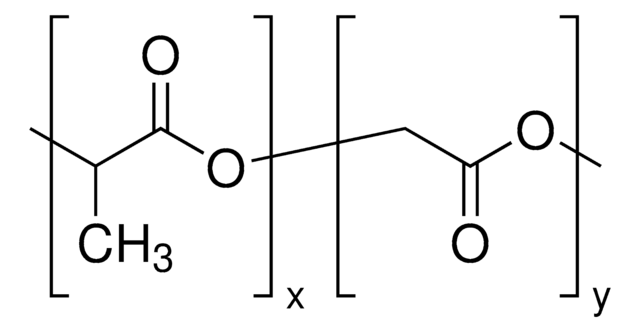
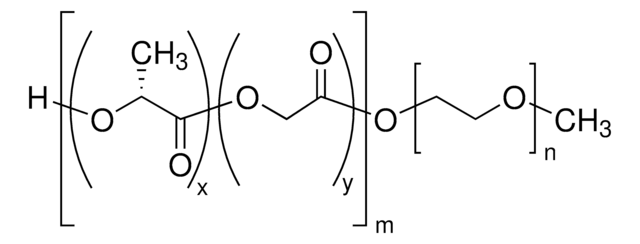
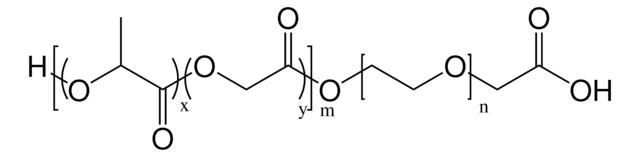
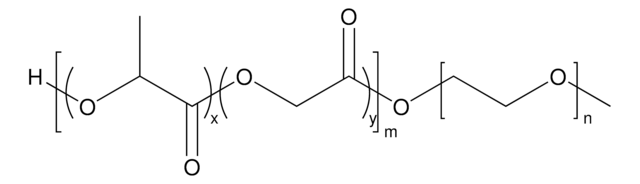
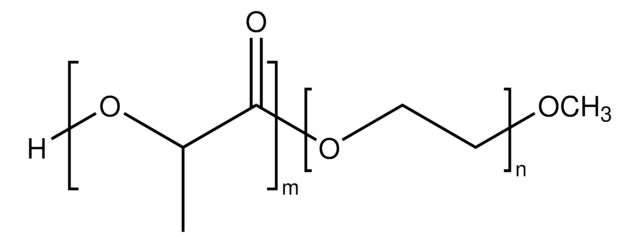
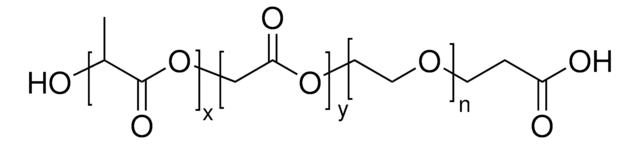
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-block-poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
PEG average Mn 5,000, PLGA Mn 55,000
Synonyme(s) :
PEG-PLGA, Polyethylene glycol, mPEG-b-PLGA, mPEG-b-PLGA
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Description
typical PEG PDI < 1.1; overall PDI < 2.5
Niveau de qualité
Forme
pellets
Ratio alimentaire
lactide:glycolide 50:50
Poids mol.
PEG average Mn 5,000
PLGA Mn 55,000
average Mn 60,000 (total)
Intervalle de dégradation
1-4 weeks
Température de transition
Tg 10 °C(lit.)
Tm 254-259 °C
PDI
<1.2
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Caractéristiques et avantages
- Good biocompatibility, low immunogenicity and good degradability.
- Properties can be easily modulated by changing the block copolymer segment sizes to suit a particular application.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
One of the common difficulties with intravenous drug delivery is low solubility of the drug. The requirement for large quantities of saline to dissolve such materials limits their clinical use, and one solution for this problem that has recently generated interest is the formation of drug-loaded micelles.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
Microparticle drug delivery systems have been extensively researched and applied to a wide variety of pharmaceutical and medical applications due to a number of advantages including injectability, local applicability to target tissues and sites, and controlled drug delivery over a given time period.
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique