675288
PEDOT
nanoparticles, aqueous dispersion
Synonyme(s) :
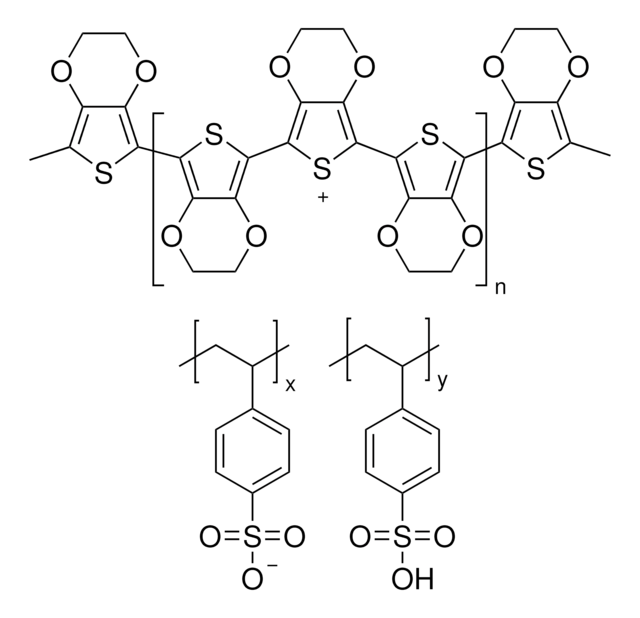
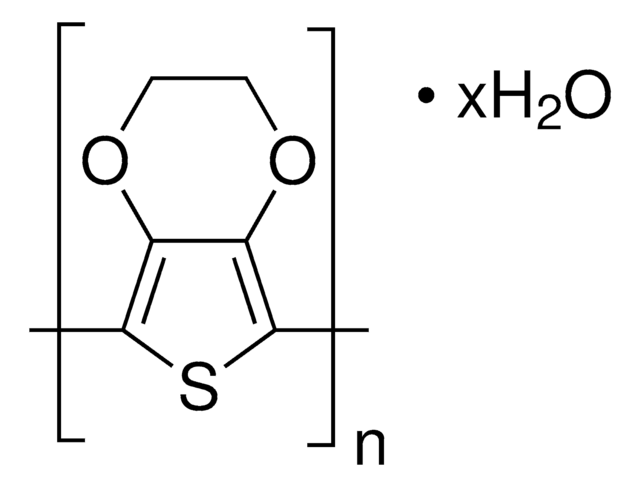
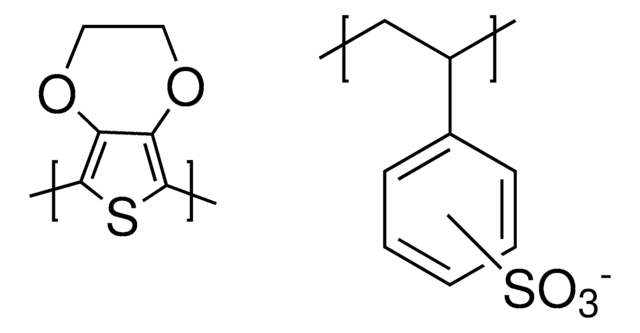
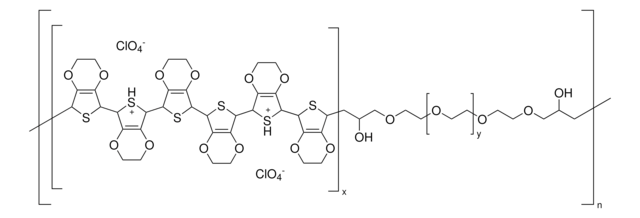
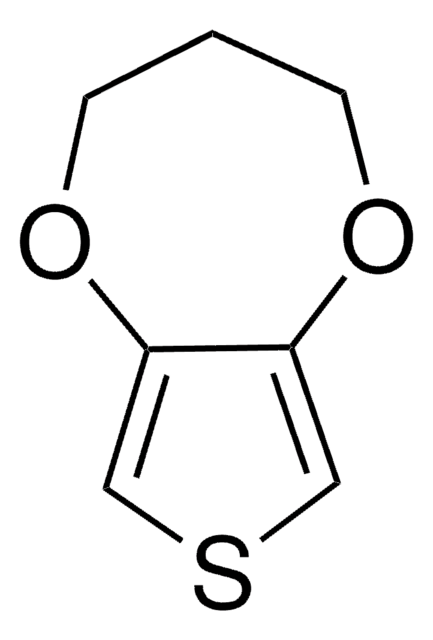
PEDOT, Poly(2,3-dihydrothieno-1,4-dioxin)
About This Item
Produits recommandés
product name
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), nanoparticles, dispersion, in H2O
Forme
dispersion
nanoparticles
Niveau de qualité
Contient
dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid (DBSA) as dopant
Concentration
in H2O
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Conjugated polymers offer charge transport between inorganic, electrically conducting metals and organic, proton-conducting biological systems.
Progress in Organic Thermoelectric Materials & Devices including high ZT values of >0.2 at room temperature by p-type (PEDOT:PSS) & n-type (Poly[Kx(Ni-ett)]) materials are discussed.
Professor Rivnay (Northwestern University, USA) discusses using organic mixed conductors as an alternative to efficiently bridge the ionic world of biology with contemporary microelectronics.
The application of conducting polymers at the interface with biology is an exciting new trend in organic electronics research.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique