926485
Phase Guide Mixer Chip
Fluidic 533, COC
Synonym(s):
Microfluidic chip
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
Microfludic chip x1
Application
The Phase Guide Mixer Fluidic 533 COC microfluidic chip applies passive phaseguided mixing principles and is not meant to be used in flow-through mode.
Features and Benefits
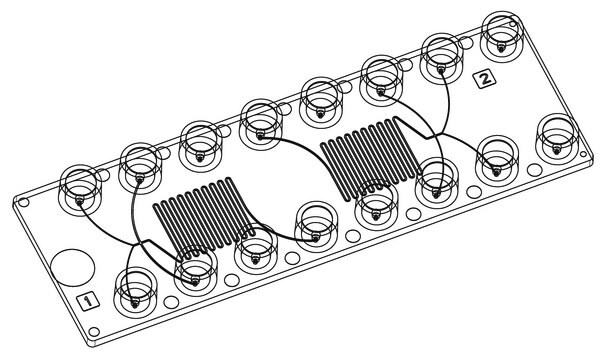
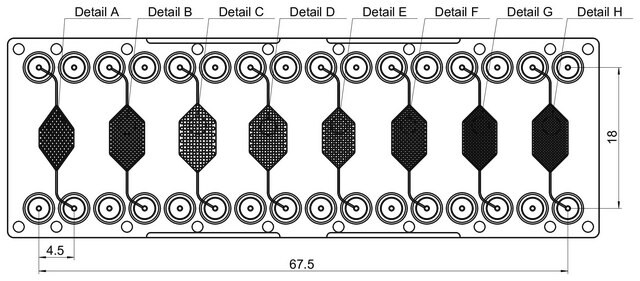
- Three varying micromixing units per chip
- Each unit features three inlets and one outlet
- Phaseguide technology provides complete control over the filling and emptying of microfluidic structures
Components
Chip Properties:
This mixer is based on the principles described in S. Hakenberg et al., A phaseguided passive batch microfluidic mixing chamber for isothermal amplification, Lab Chip, 12, 4576-4580, 2012.
- Mini Luer Interface
- Material: Cyclic olefin copolymer (COC)
- Volume of Chambers A & B: 5.6 μl
- Volume of Chambers C & D: 13.2 μl
- Volume of Chambers E & F: 11.1 μl
This mixer is based on the principles described in S. Hakenberg et al., A phaseguided passive batch microfluidic mixing chamber for isothermal amplification, Lab Chip, 12, 4576-4580, 2012.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Sharma T Sanjay et al.
Advanced drug delivery reviews, 128, 3-28 (2017-09-19)
Conventional systematically-administered drugs distribute evenly throughout the body, get degraded and excreted rapidly while crossing many biological barriers, leaving minimum amounts of the drugs at pathological sites. Controlled drug delivery aims to deliver drugs to the target sites at desired
Dongfei Liu et al.
Lab on a chip, 17(11), 1856-1883 (2017-05-10)
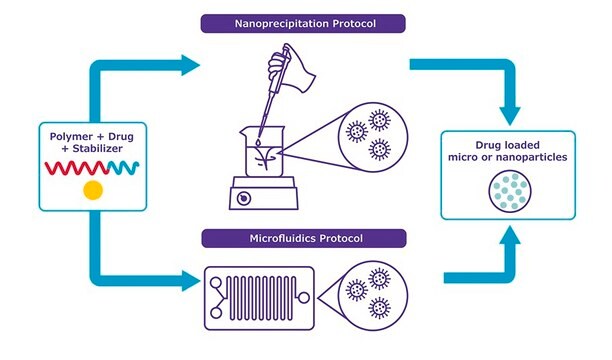
The microfluidic technique has brought unique opportunities toward the full control over the production processes for drug delivery carriers, owing to the miniaturisation of the fluidic environment. In comparison to the conventional batch methods, the microfluidic setup provides a range
Articles
Microfluidic assembly can efficiently overcome the general disadvantages of polyamine nanoencapsulation of nucleic acids, such as a less defined morphology and composition, polydispersity, and poor reproducibility.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service