926361
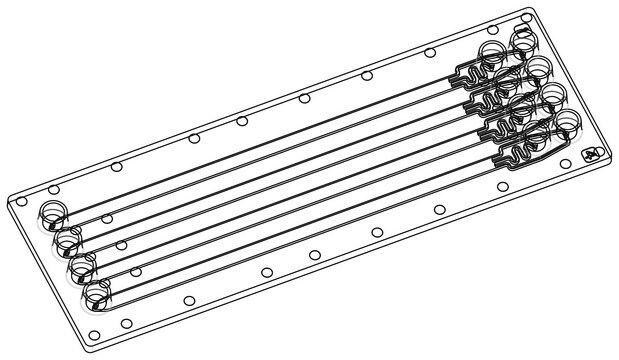
Diffusion mixer chip
Fluidic 186, PC
Synonym(s):
Microfluidic chip
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
Microfludic chip x1
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
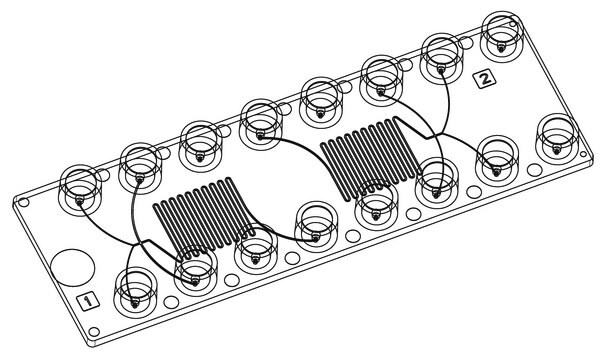
Application
- Two identical micromixing units per chip
- Each unit feature four inlets and one outlet
- The micromixing units can be daisy chained to further improve mixing
Components
- Luer Interface
- Material: Polycarbonate (PC)
- Channel Depth: 100 μm
- Channel Width Inlets: 100/200 μm
- Channel Width Mixer: 200 μm
- Channel Width Outlet: 200 μm
- Volume Mixing Channel: 4.11 μL
- Length of mixing channel: 217 mm
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
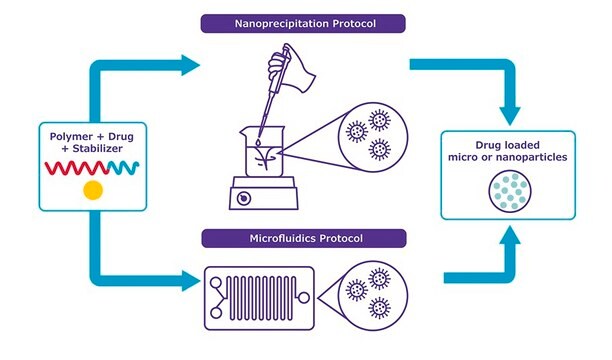
Microfluidic assembly can efficiently overcome the general disadvantages of polyamine nanoencapsulation of nucleic acids, such as a less defined morphology and composition, polydispersity, and poor reproducibility.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service