Alle Fotos(2)
Wichtige Dokumente
V900891
Collagenase aus Clostridium histolyticum
Type I, for general use, Vetec™, reagent grade, powder, ≥125 CDU/mg solid
Synonym(e):
Clostridiopeptidase A
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(2)
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
reagent grade
Produktlinie
Vetec™
Form
powder
Spezifische Aktivität
≥125 CDU/mg solid
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
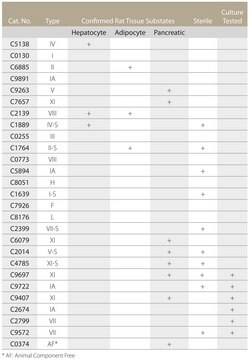
Collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum may be used for the isolation of cells from many types of animal tissue. VETEC Collagenase Type I has the original balance of collagenase, caseinase, clostripain, and tryptic activities, and is suggested for epithelial, liver, lung and adrenal primary cell isolations.
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Collagenase wird durch vier Grammatom Calcium pro Mol Enzym aktiviert. Sie wird durch Ethylenglycol-bis-(beta-aminoethylether)-N, N, N′,N′-tetraessigsäure, β-Mercaptoethanol, Glutathion, Thioglycolsäure und 8-Hydroxychinolin gehemmt.
Qualität
Also contains clostripain, nonspecific neutral protease, and tryptic activities.
Einheitendefinition
Eine Collagen-Aufschlusseinheit (Collagen Digestion Unit, CDU) setzt Peptide aus Rinder-Achillessehnencollagen entsprechend der Ninhydrin-Anfärbung von 1,0 μmol Leucin in 5 Stunden bei pH 7,4 und 37 °C in Gegenwart von Calciumionen frei. Eine FALGPA-Hydrolyseeinheit hydrolysiert 1,0 μmol Furylacryloyl-Leu-Gly-Pro-Ala pro Minute bei 25 °C. Eine neutrale Protease-Einheit hydrolysiert die Caseinmenge, die eine Färbung entsprechend 1,0 μmol Tyrosin pro 5 Stunden bei pH 7,5 und 37 °C produziert. Eine Clostripain-Einheit hydrolysiert 1,0 μmol BAEE pro Minute bei pH 7,6 und 25 °C in Gegenwart von DTT.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Vetec is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Xiaowu Wang et al.
Frontiers in pharmacology, 12, 731609-731609 (2021-11-23)
The incidence of cardiovascular diseases was significantly increased in postmenopausal women. The protection of estrogen in the cardiovascular system has been further reported for decades. Although menopausal hormone therapy has been used in many clinical trials, the debatable results indicate
Mingle Dou et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 295(15), 4937-4949 (2020-03-11)
Mammalian skeletal muscles comprise different types of muscle fibers, and this muscle fiber heterogeneity is generally characterized by the expression of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) isoforms. A switch in MyHC expression leads to muscle fiber-type transition under various physiological and
Haijian Cai et al.
Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology, 80(1), 95-109 (2022-05-06)
Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) is an active form of artemisinin extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Artemisia annua , which is used to treat malaria. Previous studies have shown that DHA has a therapeutic effect on pulmonary hypertension (PH), but its specific
Bing Zhang et al.
Cell death & disease, 10(7), 520-520 (2019-07-10)
C1q-tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 (CTRP3) is an adipokine, which exerts protective function in ischemic or diabetic heart injury. However, the role of CTRP3 in cardiac hypertrophy remains unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the pharmacological effects of
Bing Zhang et al.
Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2020, 9187065-9187065 (2021-01-12)
Mitochondrial unfolding protein response (UPRmt) effectively resists the pathological cardiac hypertrophy and improves the mitochondrial function. However, the specific activation mechanism and drugs that can effectively activate UPRmt in the cardiac muscle are yet to be elucidated. The aim of
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.