SRP6415
Cathepsin D human
recombinant, expressed in HEK 293 cells, ≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonym(e):
CLN10, CPSD, CTSD
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Biologische Quelle
human
Rekombinant
expressed in HEK 293 cells
Markierung
6-His tagged (C-terminus)
Assay
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Form
lyophilized
Mol-Gew.
calculated mol wt 43.6 kDa
observed mol wt 45-55 kDa (DTT-reduced. Protein migrates due to glycosylation. Ser 19 is the predicted N-terminal.)
Verpackung
pkg of 10 μg
Hersteller/Markenname
Sigma-Aldrich
Lagerbedingungen
dry at room temperature
Methode(n)
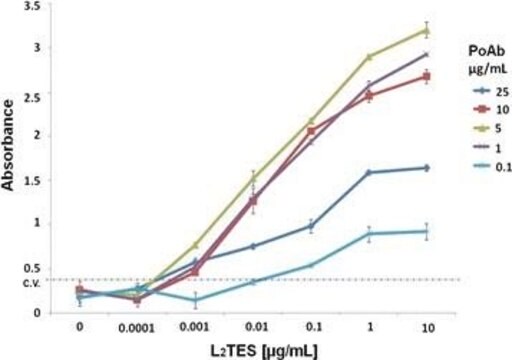
activity assay: suitable
Verunreinigungen
<1 EU/μg endotoxin (LAL test)
Eignung
suitable for molecular biology
UniProt-Hinterlegungsnummer
Anwendung(en)
life science and biopharma
Versandbedingung
wet ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Angaben zum Gen
human ... CTSD(1509)
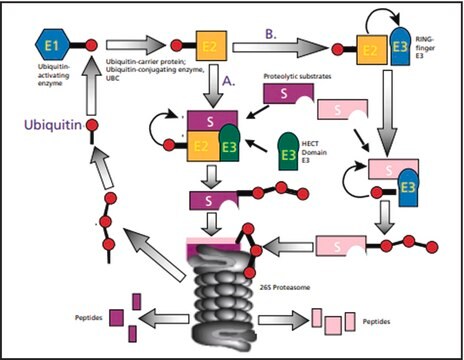
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Physikalische Form
Rekonstituierung
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Leider sind derzeit keine COAs für dieses Produkt online verfügbar.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.