Alle Fotos(2)
Wichtige Dokumente
RAB0464
Mouse Thrombopoietin ELISA Kit
for serum, plasma and cell culture supernatant
Synonym(e):
TPO
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC-Code:
41116158
NACRES:
NA.32
Empfohlene Produkte
Speziesreaktivität
mouse
Verpackung
kit of 96 wells (12 strips x 8 wells)
Methode(n)
ELISA: suitable
capture ELISA: suitable
Aufnahme
sample type plasma
sample type cell culture supernatant(s)
sample type serum
assay range
inter-assay cv: <12%
intra-assay cv: <10%
sensitivity: 30 pg/mL
standard curve range: 27.4-20000 pg/mL
Nachweisverfahren
colorimetric
Versandbedingung
wet ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Angaben zum Gen
mouse ... Thpo(21832)
Allgemeine Beschreibung
The Mouse TPO ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of mouse TPO in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine.
Immunogen
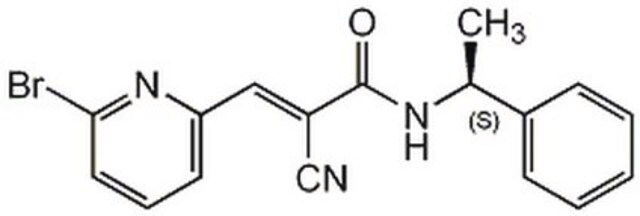
Recombinant Mouse Thrombopoietin
Anwendung
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Sonstige Hinweise
A sample Certificate of Analysis is available for this product.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Kit-Komponenten auch einzeln erhältlich
Produkt-Nr.
Beschreibung
SDB
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
P-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Met. Corr. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Helena Tizón-Marcos et al.
The American journal of cardiology, 114(7), 1094-1099 (2014-08-19)
Increased myocardial trabeculations define noncompaction cardiomyopathy (NCC). Imaging advancements have led to increasingly common identification of prominent trabeculations with unknown implications. We quantified and determined the impact of trabeculations' burden on cardiac function and stretch in a population of healthy
Nike Müller et al.
PloS one, 9(4), e94282-e94282 (2014-04-15)
Inflammation and metabolism have been shown to be evolutionary linked and increasing evidence exists that pro-inflammatory factors are involved in the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Until now, most data suggest that within adipose tissue these factors are
Y-L Zhang et al.
Letters in applied microbiology, 59(6), 580-586 (2014-08-29)
Clostridium sporogenes ATCC 3584 is an obligate anaerobe that has been reported to possess excellent tumour-targeting capacity. Here, we use Cl. sporogenes as a vector to deliver IL-12, a potent antitumour cytokine that bears numerous antitumour properties but that has limited
Irene Ciancarelli et al.
Biomarkers : biochemical indicators of exposure, response, and susceptibility to chemicals, 19(6), 452-456 (2014-07-02)
Peripheral oxidative biomarkers could be useful for monitoring clinical features of Huntington's disease (HD). Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD), neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxoGua) serum levels were analysed in 18 HD patients and 10 controls. Clinical measures were recorded from each
Sangbin Park et al.
PLoS genetics, 10(8), e1004555-e1004555 (2014-08-08)
Insulin is a major regulator of metabolism in metazoans, including the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) suggest a genetic basis for reductions of both insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion, phenotypes commonly observed in humans with type 2
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.