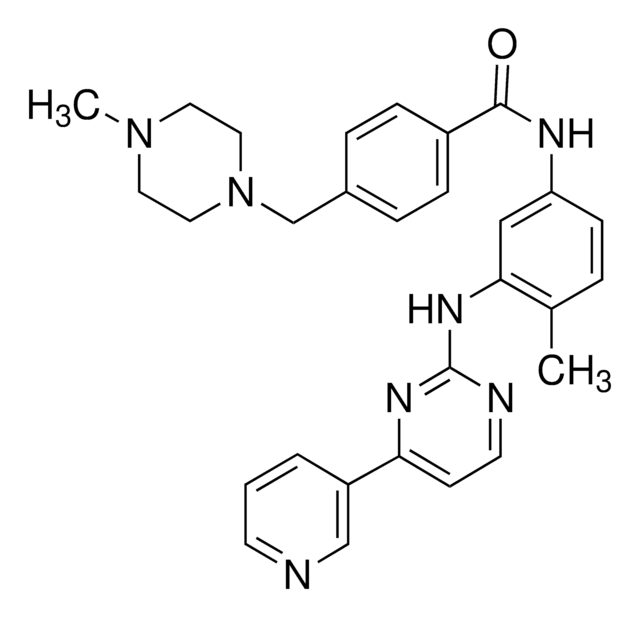
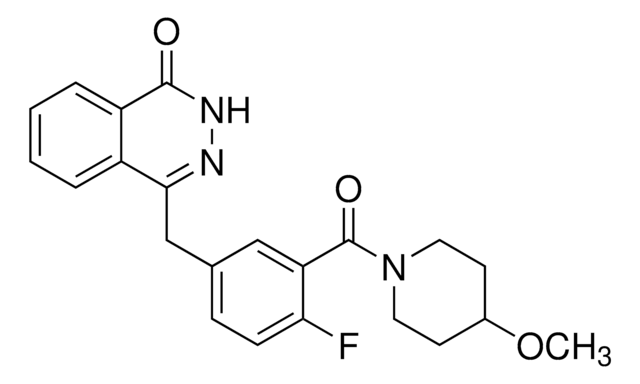
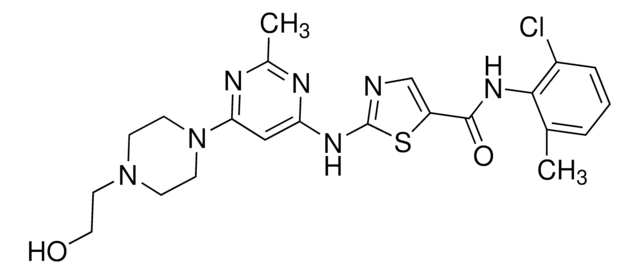
PZ0242
PF-06658607
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(e):
(R)-1-(3-(4-Amino-3-(4-(3-ethynylphenoxy)phenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, Ibrutinib-yne, Probe 4
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
Form
powder
Farbe
white to beige
Löslichkeit
DMSO: 20 mg/mL, clear
Lagertemp.
room temp
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Die passende Version wird nicht angezeigt?
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Version benötigen, können Sie anhand der Lot- oder Chargennummer nach einem spezifischen Zertifikat suchen.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Verwandter Inhalt
The aim of the Cravatt research group is to understand the roles that mammalian enzymes play in physiological and pathological processes and to use this knowledge to identify novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of human disease. To achieve these goals, they develop and apply new technologies that bridge the fields of chemistry and biology, ascribing to the philosophy that the most significant biomedical problems require creative multidisciplinary approaches for their solution. The group's technological innovations address fundamental challenges in systems biology that are beyond the scope of contemporary methods. For instance, enzymes are tightly regulated by post-translational events in vivo, meaning that their activity may not correlate with expression as measured by standard genomic and proteomic approaches. Considering that it is an enzyme's activity, rather than abundance that ultimately dictates its role in cell physiology and pathology, the Cravatt group has introduced a set of proteomic technologies that directly measures this parameter. These activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) methods exploit the power of chemistry to engender new tools and assays for the global analysis of enzyme activities. The enzyme activity profiles generated by ABPP constitute unique molecular portraits of cells and tissues that illuminate how metabolic and signaling networks are regulated in vivo. Additionally, by evaluating enzymes based on functional properties rather than mere abundance, ABPP acquires high-content proteomic information that is enriched in novel markers and targets for the diagnosis and treatment of human disease.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.



![Tris[(1-Benzyl-1H-1,2,3-Triazol-4-yl)methyl]amin 97%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/179/695/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f/640/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f.png)