Anwendung
Alkalische Phosphatase kann zur Dephosphorylierung von Kasein und anderen Proteinen verwendet werden. Außerdem kann die alkalische Phosphatase zur Dephosphorylierung des 5′-Endes der DNA oder RNA verwendet werden, um Selbstligation zu vermeiden. DNA oder RNA kann nach der Dephosphorylierung mit alkalischer Phosphatase auch mit radiomarkiertem Phosphat (über die T4-Polynukleotidkinase) markiert werden.
Durch die hohe spezifische Aktivität empfohlen für konjugierte Antikörper und Proteine.
Alkaline phosphatase is usually conjugated to antibodies and other proteins in immunological techniques such as ELISA, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. It is routinely used to dephosphorylate proteins and nucleic acids. It may be used for protein labeling when high sensitivity is required. Alkaline phosphatase may be also be used to dephosphorylate the 5′-termini of DNA or RNA to prevent self-ligation. DNA or RNA can also be tagged with radiolabeled phosphate (via T4 polynucleotide kinase) after dephosphorylation with alkaline phosphatase. Product P7923 has been used in a novel screening strategy for nitrilase-producing strains.
The enzyme has been used to develop a highly sensitive immunoassay for determining one thousandth of an attomole (1 zeptomole) of alkaline phosphatase. It has been used in an immunoassay of proinsulin. It has also been used to pretreat ISG (immature secretory granule) membranes to study the phosphorylation of proteinacous components in it.
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Das Enzym weist eine weite Spezifität für Phosphatester von Alkoholen, Aminen, Pyrophosphaten und Phenolen auf. Es kommt routinemäßig bei der Dephosphorylierung von Proteinen und Nukleinsäuren zum Einsatz.
Alkaline phosphatase, from bovine intestinal mucosa, is most stable in the pH range 7.5-9.5. The enzyme has a broad specificity for phosphate esters of alcohols, amines, pyrophosphate, and phenols. It requires zinc, and magnesium or calcium divalent ions for activity.
The enzyme is a glycoprotein containing approximately 12% carbohydrate (6% hexoses and 6% other neutral sugars). Each molecule of alkaline phosphatase contains four zinc atoms and four disulfide bridges. Maximal activity with alkaline phosphatase is achieved in the presence of magnesium. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters such as: p-nitrophenyl phosphate, phenyl phosphate, phenolphthalein phosphate, α-glycerol phosphate, β-glycerol phosphate, 2-phosphorylglycerate, triosephosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, glucose 1-phosphate, fructose 1-phosphate, fructose 6-phosphate, adenosine 5-phosphate adenosine 3-phosphate, phosphoenolpyruvate, and β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. Arsenate, cysteine, iodine, inorganic phosphate, pyrophosphate, diisopropyl phosphate, triphenylphosphate, diisopropyl fluorophosphate, and L-phenylalanine are some of the strong inhibitors of alkaline phosphatase.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
Die intestinale alkalische Phosphatase vom Rind ist ein dimeres Glykoprotein auf Membranbasis. Es sind mindestens drei Isoforme vorhanden, die üblicherweise zwei N-verknüpfte und ein oder mehrere O-verknüpfte Glykane pro Monomer besitzen.
Die intestinale alkalische Phosphatase vom Rind ist ein dimeres Glykoprotein auf Membranbasis. Es sind mindestens drei Isoforme vorhanden, die üblicherweise zwei N-verknüpfte und ein oder mehrere O-verknüpfte Glykane pro Monomer besitzen.2 Für die Aktivität dieses Enzyms sind Zink und zweiwertige Magnesium- oder Calcium-Ione erforderlich.
Einheitendefinition
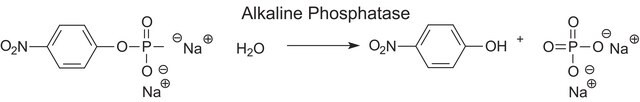
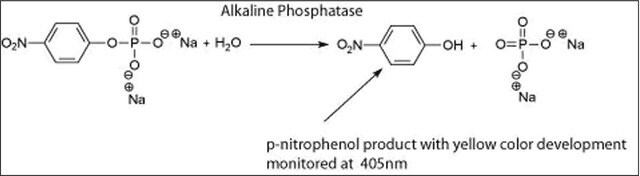
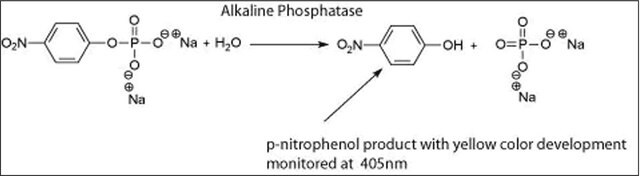
Eine DEA-Einheit hydrolysiert 1 μmol 4-Nitrophenylphosphat pro Minute bei einem pH-Wert von 9,8 und 37 °C. (Eine Glycin-Einheit entspricht ungefähr 3 DEA-Einheiten.)
Physikalische Form
Solution in 40% glycerol containing 6 mM Tris/HCl, 6 mM MgCl2 and 0.12 mM ZnCl2, ~pH 7.6
Hinweis zur Analyse
Packungsgrössen basieren auf DEA-Einheiten
Protein determined by biuret.