Alle Fotos(1)
Wichtige Dokumente
F0137
Fructose-6-phosphate Kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus
Type VII, lyophilized powder, ≥50 units/mg protein
Synonym(e):
6-Phosphofructokinase, ATP:D-fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Typ
Type VII
Qualitätsniveau
Form
lyophilized powder
Spezifische Aktivität
≥50 units/mg protein
Mol-Gew.
34 kDa
Versandbedingung
wet ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Fructose-6-phosphate kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus, a 34 kDa enzyme, belongs to phosphofructokinase (PFK) - like superfamily. The glutamate 161 and arginine 162 residues at the active site are crucial for substrate binding.
Research Area: Cell Signaling
Bacillus stearothermophilus phosphofructokinase (BsPFK) is a homotetramer that is allosterically inhibited by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), which binds along one dimer-dimer interface.
Bacillus stearothermophilus phosphofructokinase (BsPFK) is a homotetramer that is allosterically inhibited by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), which binds along one dimer-dimer interface.
Anwendung
Fructose-6-phosphate Kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus was shown to interact with neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) causing a defect in glycolytic metabolism and increased fatigability in dystrophic muscle.
Fructose-6-phosphate Kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus has been used in the assay mixture for mass spectrometry assay for phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI) (G6P to F6P reaction).
Fructose-6-phosphate kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus has been used:
- in steady state analysis of phosphofructokinase activity in the presence of ATP deuterated at the C8 position(C8-D ATP)
- for standard curve generation for quantifying muscle phosphofructokinase (PFK) activity
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
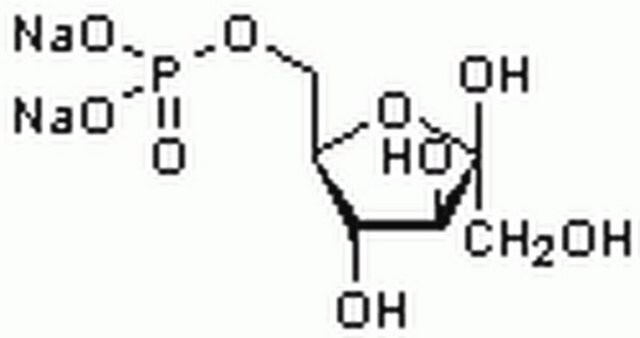
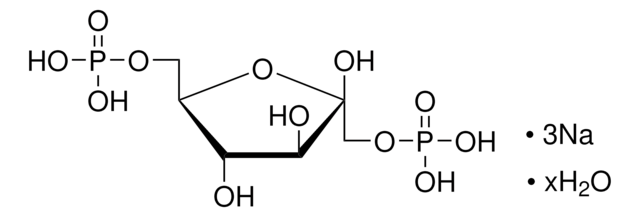
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBP) is an important enzyme in glucose metabolism. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate. Fructose-6-phosphate kinase converts fructose-6-phosphate into fructose 1,6-bisphophate in the rate limiting step of the glycolysis cycle.
Phosphofructokinase (PFK) is an essential bifunctional enzyme that serves as a critical regulator in the intermediate stages of glycolysis. PFK is strongly linked to caveolae and is brought to caveolae by caveolin-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs).
Einheitendefinition
One unit will convert 1.0 μmole of fructose 6-phosphate and ATP to fructose 1,6-diphosphate and ADP per minute at pH 9.0 at 30 °C.
Physikalische Form
Lyophilized powder containing buffer salt (e.g. phosphate buffer, or Tris buffer with NaCl)
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Loss of positive allosteric interactions between neuronal nitric oxide synthase and phosphofructokinase contributes to defects in glycolysis and increased fatigability in muscular dystrophy
Wehling-Henricks M, et al.
Human Molecular Genetics, 18(18), 3439-3451 (2009)
Rockann Mosser et al.
Biochemistry, 52(32), 5421-5429 (2013-07-19)
Bacillus stearothermophilus phosphofructokinase (BsPFK) is a homotetramer that is allosterically inhibited by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), which binds along one dimer-dimer interface. The substrate, fructose 6-phosphate (Fru-6-P), binds along the other dimer-dimer interface. Evans et al. observed that the structure with inhibitor
Analysis of the phosphofructokinase subunits and isoenzymes in human tissues
G.A. Dunaway et al.
The Biochemical Journal, 251, 755-757 (1988)
Chunsheng Liu et al.
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology, 307(7), G749-G759 (2014-08-30)
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling are required for hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation under pathological conditions such as liver metastatic tumor growth. These two signaling pathways are functionally divergent; PDGF signaling promotes proliferation and migration
M Hattori et al.
Nature, 405(6784), 311-319 (2000-06-01)
Chromosome 21 is the smallest human autosome. An extra copy of chromosome 21 causes Down syndrome, the most frequent genetic cause of significant mental retardation, which affects up to 1 in 700 live births. Several anonymous loci for monogenic disorders
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.