C4461
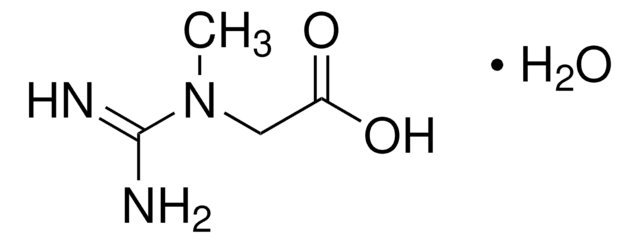
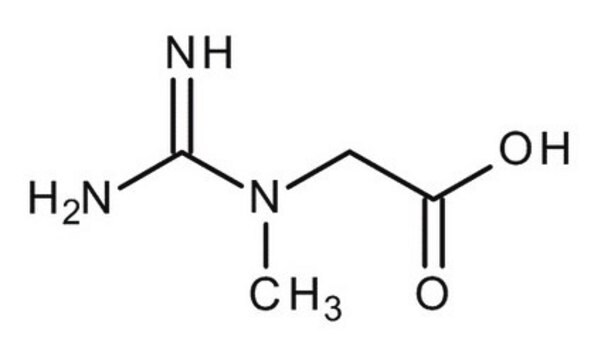
Colistin -sulfat (Salz)
≥19,000 IU/mg
Synonym(e):
Polymyxin E
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
powder
Qualitätsniveau
Spezifische Aktivität
≥19,000 IU/mg
Wirkungsspektrum von Antibiotika
Gram-negative bacteria
Wirkungsweise
cell membrane | interferes
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C53H100N16O13.H2O4S/c1-9-30(6)12-10-11-13-41(72)60-33(14-20-54)48(77)69-43(32(8)71)53(82)65-36(17-23-57)45(74)64-38-19-25-59-52(81)42(31(7)70)68-49(78)37(18-24-58)62-44(73)34(15-21-55)63-50(79)39(26-28(2)3)67-51(80)40(27-29(4)5)66-46(75)35(16-22-56)61-47(38)76;1-5(2,3)4/h28-40,42-43,70-71H,9-27,54-58H2,1-8H3,(H,59,81)(H,60,72)(H,61,76)(H,62,73)(H,63,79)(H,64,74)(H,65,82)(H,66,75)(H,67,80)(H,68,78)(H,69,77);(H2,1,2,3,4)/t30?,31-,32-,33+,34+,35+,36+,37+,38+,39+,40-,42+,43+;/m1./s1
InChIKey
ZJIWRHLZXQPFAD-LRYSGCCDSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
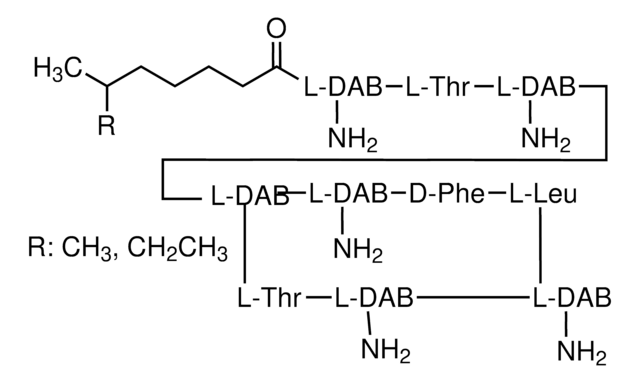
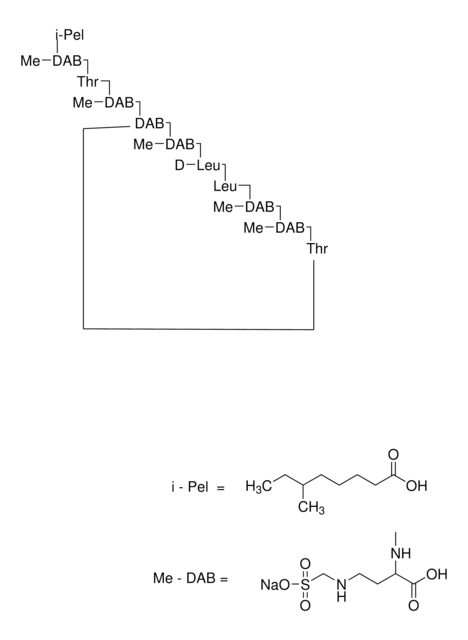
Antimikrobielles Spektrum: Gram-negative Bakterien.
Antimikrobielles Spektrum: Gramnegative Bakterien. Die Colistinresorption der Nieren soll möglicherweise organische Kationen- und Peptidtransporter umfassen und der Prozess soll pH-empfindlich sein .
Hinweis zur Analyse
Sonstige Hinweise
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
P-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.