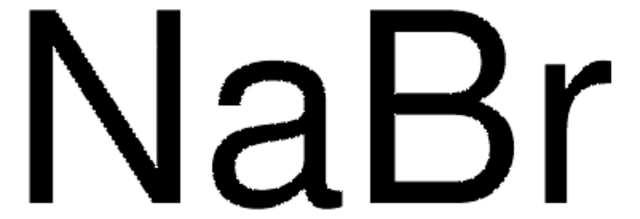Wichtige Dokumente
746401
Natriumbromid
anhydrous, free-flowing, Redi-Dri™, ReagentPlus®, ≥99%
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
anhydrous
free-flowing
Qualitätsniveau
Dampfdruck
1 mmHg ( 806 °C)
Produktlinie
ReagentPlus®
Redi-Dri™
Assay
≥99%
Form
powder
pH-Wert
5.4 (20 °C, 50 g/L)
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
755 °C (lit.)
SMILES String
[Na+].[Br-]
InChI
1S/BrH.Na/h1H;/q;+1/p-1
InChIKey
JHJLBTNAGRQEKS-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
Towards greener solvents for the bleach oxidation of alcohols catalysed by stable N-oxy radicals
Rechtliche Hinweise
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Repr. 2 - STOT RE 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Central nervous system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.