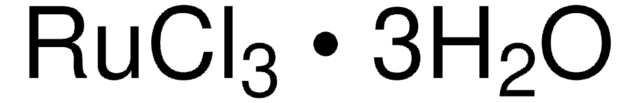931578
Ruthenium(III)-chlorid Hydrat
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(e):
Ruthenium trichloride, Trichlororuthenium hydrate
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Form
powder
Verunreinigungen
≤1000.0 ppm (trace metals analysis)
Löslichkeit
acetone: soluble ((lit.))
ethanol: soluble
water: soluble
Dichte
3.11 g/cm3
SMILES String
O.Cl[Ru](Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/3ClH.H2O.Ru/h3*1H;1H2;/q;;;;+3/p-3
InChIKey
BIXNGBXQRRXPLM-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Industrially, ruthenium trichloride hydrate is produced by dissolving ruthenium oxides in hydrochloric acid. The hydrated salt is obtained by recrystallization.
Anwendung
Another common application of ruthenium chloride hydrate is as a precursor for single-atom catalysts. For example, scientists have used ruthenium chloride hydrate for the synthesis of ruthenium single-atom-doped ZrO2 particles to catalyze nitrogen fixation and for the synthesis of ruthenium single-atom-doped MXenes to catalyze hydrogen evolution. A third common application of ruthenium chloride hydrate is in the synthesis of metal alloys, like PtRuIr, or PtRuFe, which are investigated for electrocatalysis, usually the oxidation of simple organics like methanol or formic acid.
For use in all these applications, also consider our higher-purity ruthenium chloride hydrate, 463779, with trace metals purity greater than 99.98%, which offers the best reproducibility and purity.
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Lagerklassenschlüssel
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Leider sind derzeit keine COAs für dieses Produkt online verfügbar.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.