C85409
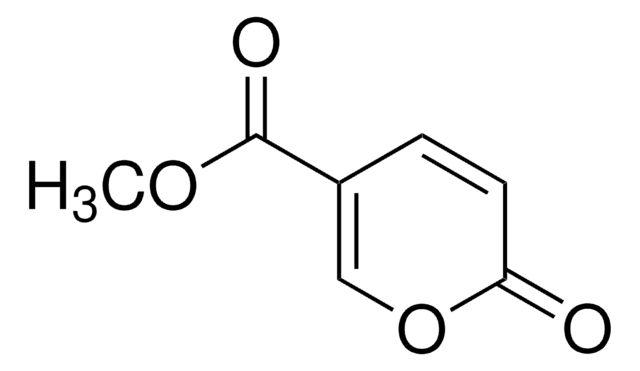
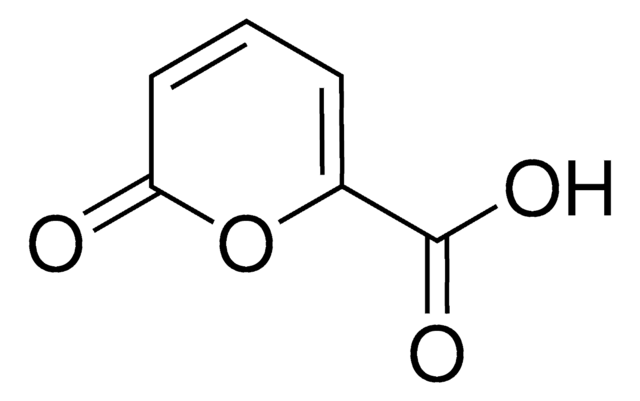
Coumalic acid
97%
Synonym(s):
2-Oxo-2H-pyran-5-carboxylic acid, 2-Pyrone-5-carboxylic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C6H4O4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
140.09
Beilstein:
119747
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
form
powder
bp
218 °C/120 mmHg (lit.)
mp
203-205 °C (dec.) (lit.)
SMILES string
OC(=O)C1=COC(=O)C=C1
InChI
1S/C6H4O4/c7-5-2-1-4(3-10-5)6(8)9/h1-3H,(H,8,9)
InChI key
ORGPJDKNYMVLFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
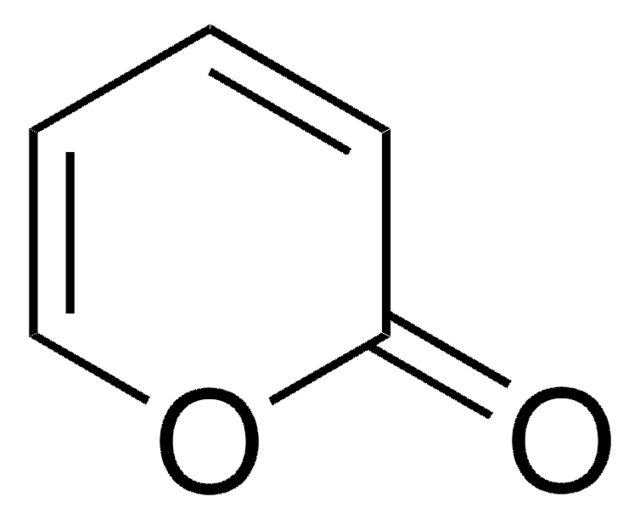
Decarboxylates to α-pyrone, a Diels-Alder diene.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
V Günzler et al.
The Biochemical journal, 242(1), 163-169 (1987-02-15)
From the structure-activity relationships of known competitive inhibitors, coumalic acid (2-oxo-1,2H-pyran-5-carboxylic acid) was deduced to be a potential syncatalytic inhibitor for chick-embryo prolyl 4-hydroxylase. The compound caused time-dependent inactivation, the reaction rate being first-order. The inactivation constant was 0.094 min-1
A Merriweather et al.
Molecular and biochemical parasitology, 116(2), 185-197 (2001-08-28)
The cuticle of parasitic nematodes consists primarily of a network of collagen molecules. The enzyme responsible for collagen maturation is prolyl 4-hydroxylase, making this enzyme a central activity in cuticle biosynthesis and a potentially important chemotherapeutic target. Adult and embryonic
Weijun Chen et al.
International journal of food sciences and nutrition, 63(2), 236-241 (2011-09-29)
The oxidative modification of human low density lipoprotein (LDL) plays a significant role in atherosclerosis. In this study, the inhibiting activity of areca inflorescence extracts (AIEs) on LDL oxidation was investigated by an in vitro study with Trolox as the
Yongxia Li et al.
Phytopathology, 110(4), 805-812 (2020-03-03)
Poplar canker, mainly caused by Botryosphaeria species, is a serious disease that has resulted in the reduced productivity and death of poplar worldwide. Different Populus species have varied resistance levels to poplar canker; however, whether phenolic compounds in poplar are
Michio Ohi et al.
Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry, 67(1), 170-173 (2003-03-07)
Some chemicals were examined for their effects on the germination of resting spores of the clubroot pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae, and on the control of clubroots in Chinese cabbage. Caffeic acid, coumalic acid, and corilagin stimulated the germination of Plasmodiophora spores
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service