310808
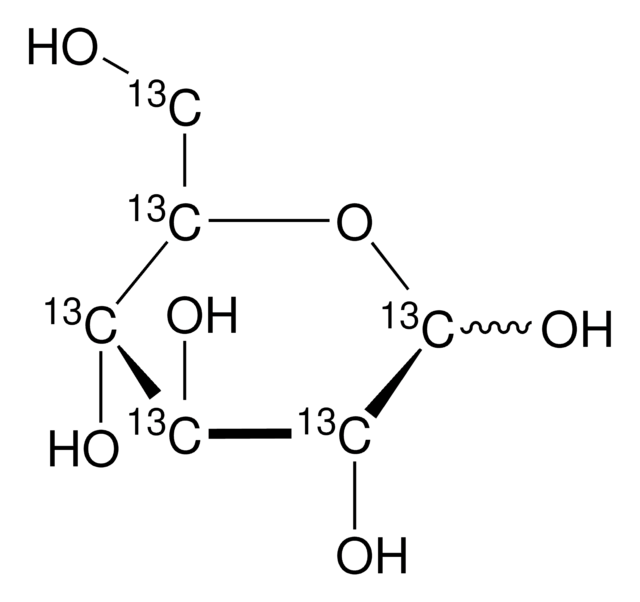
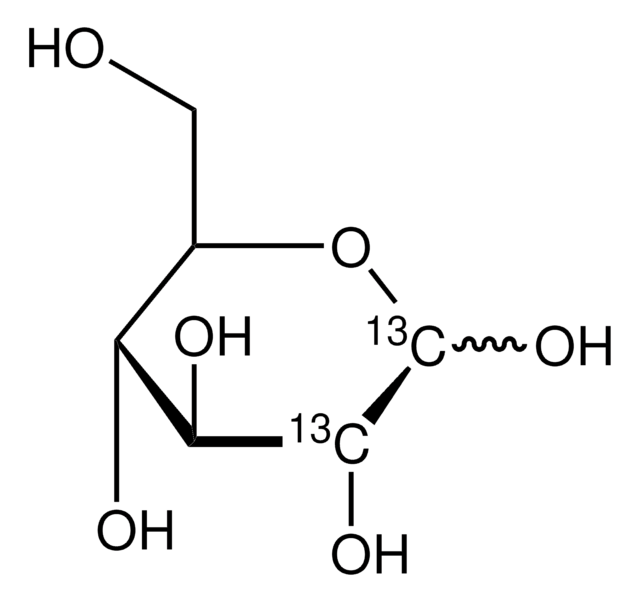
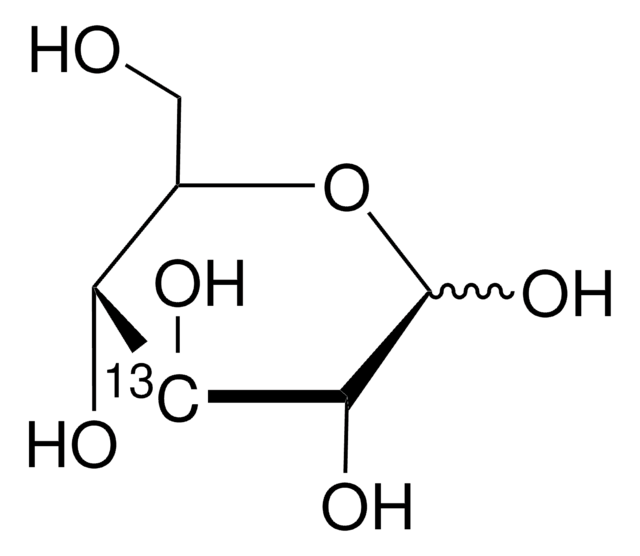
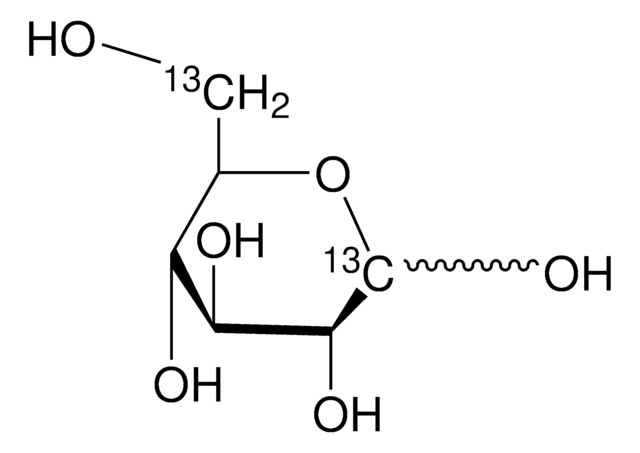
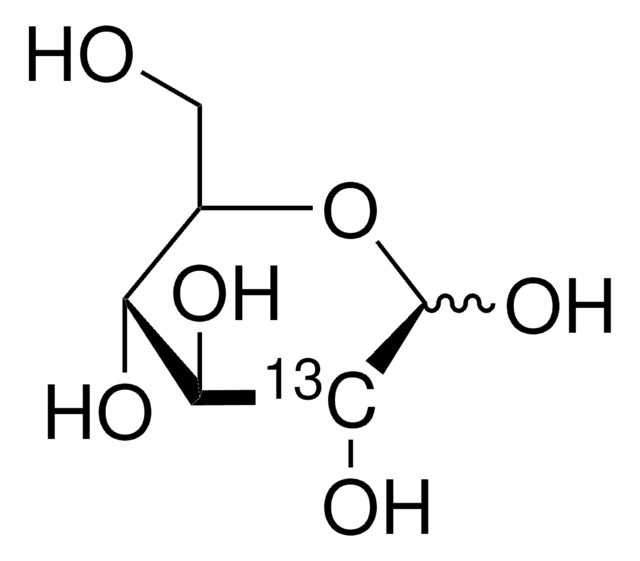
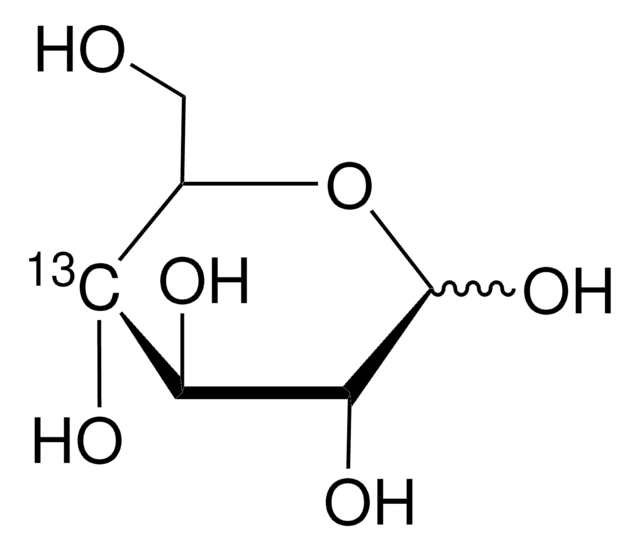
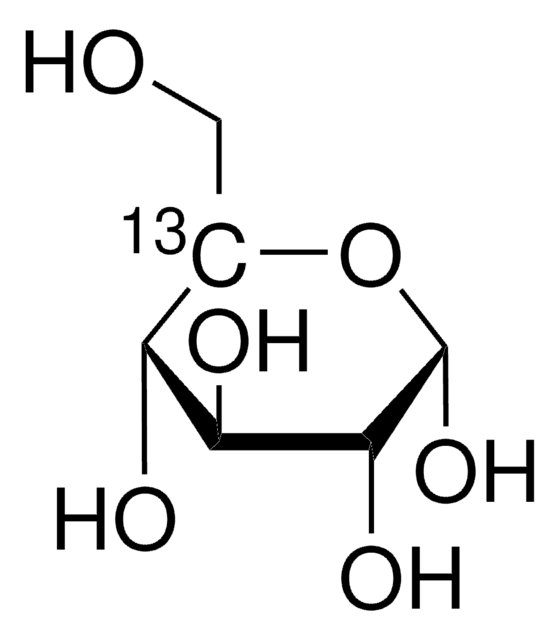
D-Glucose-6-13C
99 atom % 13C
Synonym(s):
Labeled Glucose, Dextrose-6-13C
About This Item
Recommended Products
isotopic purity
99 atom % 13C
Quality Level
Assay
99% (CP)
form
powder
optical activity
[α]25/D +52.0°, c = 2 in H2O (trace NH4OH)
mp
150-152 °C (lit.)
mass shift
M+1
SMILES string
O[13CH2][C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O
InChI
1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2/t3-,4+,5+,6+/m0/s1/i2+1
InChI key
GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-HYISWWFJSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Packaging
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Learn about monosaccharide biosynthesis and the metabolism of monosaccharides. A unit of a carbohydrate and the simplest form of a sugar, a monosaccharide cannot be hydrolyzed into a simpler compound.
Review the 10 steps of glycolysis in the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas glycolytic pathway. Easily compare reaction stages and buy the enzymes for your life science research.
Sigma-Aldrich.com presents an article concerning MRI/MRS and the use of isotopes in hyperpolarization.
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (DNP) is a phenomenon by which high spin polarization, typically derived from a bath of free radical electrons, is transferred to a nuclear spin bath, enhancing the difference between the nuclear energy levels and thereby producing dramatically enhanced NMR signals for detection.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service