P5931
Phosphatase, Alkaline from Escherichia coli
lyophilized powder, 30-60 units/mg protein (in glycine buffer)
Synonym(s):
Orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized powder
Quality Level
specific activity
30-60 units/mg protein (in glycine buffer)
composition
Protein, ~50% biuret
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) of E.coli is a member of an enzyme group that possesses intragenic complementation.
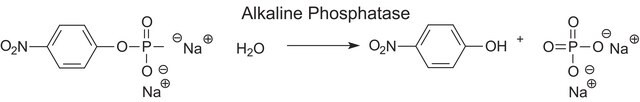
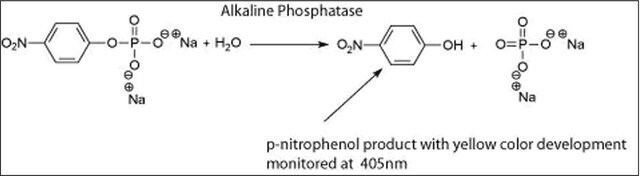
Application
Alkaline phosphatase is used for conjugation to antibodies and other proteins for ELISA, Western blotting, and histochemical detection. It may be used for protein labeling when high sensitivity is required. Product P5931 has been used during immunoblots to treat cell membranes prior to Tau1 incubation.
The enzyme from Sigma has been used to develop a synthetic nanopore membrane. This membrane mimics protein channels that are regulated by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation and uses an aligned array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) impregnated in a polystyrene matrix.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Alkaline phosphatase, from Escherichia coli, is a dimeric, non-glycosylated protein which mainly reside in the periplasmic space. Three known isoforms exist. The enzyme requires zinc, and is activated by magnesium. E. coli akaline phosphatase has a broad specificity for phosphate esters.
The enzyme is a phosphohydrolase having an optimal pH of 10 in vitro. The actual optimum pH varies depending on the nature and concentration of the substrate, the type of buffer, the phosphate acceptor, and to some extent the nature of the isoenzymes. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters such as p-nitrophenyl phosphate, phenyl phosphate, phenolphthalein phosphate, α-glycerol phosphate, β-glycerol phosphate, 2-phosphorylglycerate, triosephosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, glucose 1-phosphate, fructose 1-phosphate, fructose 6-phosphate, adenosine 5-phosphate adenosine 3-phosphate, phosphoenolpyruvate, and β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. The activity is inhibited by 1,10-phenanthroline monohydrate, diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate.
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of p-nitrophenyl phosphate per min at pH 10.4 at 37 °C.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing Tris buffer salts, MgSO4, and ZnSO4
Preparation Note
Chromatographically purified
inhibitor
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
1.Reid, T., and Wilson
E. coli Alkaline Phosphatase,The Enzymes, 3rd Ed. Vol. 4, 4, 373-373 (1971)
Characterization of Heterodimeric Alkaline Phosphatases from Escherichia coli: An Investigation of Intragenic Complementation
Hehir MJ, et al.
Journal of molecular biology, 304(4), 645-656 (2000)
A Takeda et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 275(8), 5395-5399 (2000-02-22)
Increased expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is a common feature in a number of neurodegenerative diseases. Interestingly, the spatial distribution of HO-1 expression in diseased brain is essentially identical to that of pathological expression of tau. In this study, we
Alkaline phosphatase from Thermotoga neapolitana.
A Savchenko et al.
Methods in enzymology, 331, 298-305 (2001-03-27)
R A Anderson et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 72(1), 394-397 (1975-01-01)
To facilitate the study of individual metal binding sites of polymeric metalloproteins, conversion of exchange-labile Co(II) in E. coli alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1) to exchange-inert Co(III) was examined. Oxidation of Co(II) alkaline phosphatase with hydrogen peroxide results in a single
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service