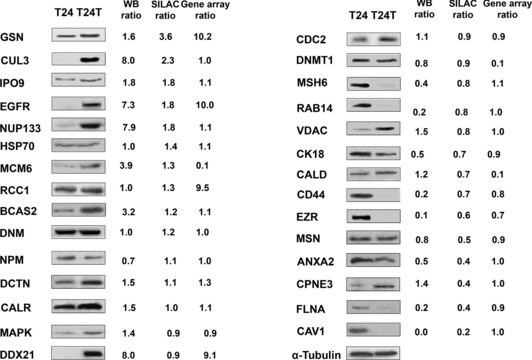
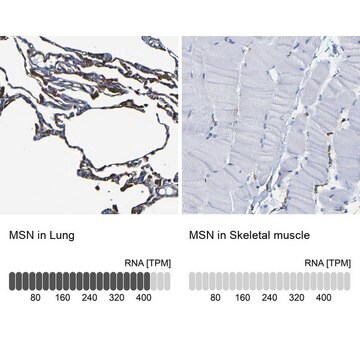
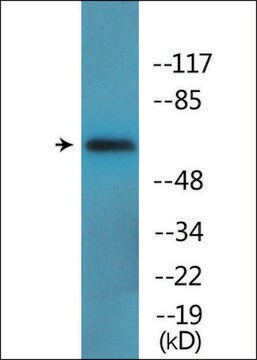
Specificity
Mouse monoclonal clone 38/87 anti-Moesin antibody recognizes the 78 kDa moesin and 80 kDa radixin molecules. It does not react with talin or ezrin. Reactivity has been reported with human, bovine, porcine, rat and mouse moesin.
Immunogen
bovine uterus moesin.
Application
Mouse monoclonal clone 38/87 anti-Moesin antibody may be used for ELISA, immunoblotting (a closely spaced doublet of 78/80 kDa) immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry (reported for frozen sections and for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections following boiling in 0.01M citrate buffer pH 6), immunocytochemistry (3.7% paraformaldehyde, 0.1% Triton X-100), flow cytometry (3-3.7% paraformaldehyde, 0.1-0.25% Triton X-100) and electron microscopy. The intensity of the fainter doublet‘s upper band seen in immunoblotting varies depending on the tissue. The antibody has been used to inhibit both the binding of proteoheparan sulfate to smooth muscle cells, and the infectivity of measles virus.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The ERM (ezrin-radixin-moesin) proteins, members of the talin-protein 4.1- merlin/schwannomin superfamily, are general cross-linkers between the plasma membrane and actin filaments. They provide such links through their N-terminal halves that associate with integral membrane proteins either directly or indirectly through adapter molecules, and through their C-terminal halves that associate with F-actin. ERM proteins are involved not only in cytoskeletal organization but also in signal transduction and apoptosis. Because their expression is regulated in a tissue-specific manner, each ERM protein has been proposed to have unique functions. There is approximately 80% homology between moesin, ezrin and radixin. These proteins are involved in a variety of cellular functions, such as cell adhesion, migration, and the organization of cell surface structures. However, moesin (in contrast to radixin and ezrin) is strongly expressed in endothelium of vessels, in T and B lymphocytes, in basal layers of squamous epithelium and glandular ducts, and in cells of carcinoma and mesothelioma. Moesin is expressed in variable amounts in cells of different phenotypes such as macrophages, lymphocytes, fibroblastic, endothelial, epithelial, and neuronal cell lines. It is overexpressed in some estrogen receptor (ER)-negative cell lines but absent from ER-positive ones, suggesting that it may play a role in the invasiveness and pattern of metastasis characteristic of ER-negative breast cancers.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.