C8849
α-Chloralose−HBC complex
≥92% α-anomer basis
Synonym(s):
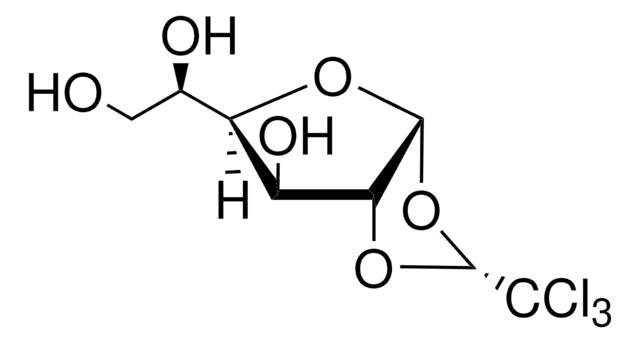
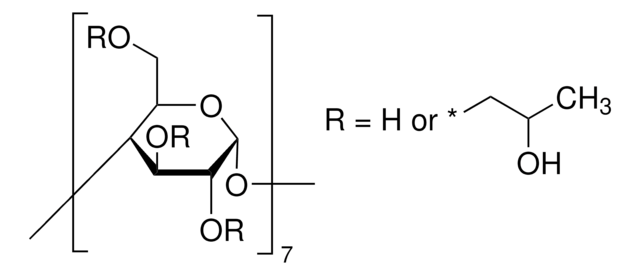
1,2-O-(2,2,2-Trichloroethylidene)-α-D-glucofuranose: 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥92% α-anomer basis
form
powder
shelf life
4 weeks at 4 °C (for aqueous solutions)
solubility
H2O: freely soluble
Application
α-Chloralose-HBC complex has been used for anesthetizing rats for various in vivo studies.
Biochem/physiol Actions
α-Chloralose-HBC complex is a preferred anesthetic over isoflurane as it displays no intrusion retinal spreading depolarization (rSD) generation and propagation.
Quality
α-Chloralose content: 10% (w/w)
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Kyle R Biesecker et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 36(36), 9435-9445 (2016-09-09)
The brain is critically dependent on the regulation of blood flow to nourish active neurons. One widely held hypothesis of blood flow regulation holds that active neurons stimulate Ca(2+) increases in glial cells, triggering glial release of vasodilating agents. This
J Silverman et al.
Laboratory animal science, 43(3), 210-216 (1993-06-01)
Chloral hydrate (CH) and alpha-chloralose (CS) are often used to anesthetize laboratory animals although, to our knowledge, there have been no controlled studies of their anesthetic or analgesic effects. Induction of and recovery from anesthesia can be stressful, and anesthesia
Tess E Kornfield et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 34(34), 11504-11513 (2014-08-22)
Light stimulation evokes neuronal activity in the retina, resulting in the dilation of retinal blood vessels and increased blood flow. This response, named functional hyperemia, brings oxygen and nutrients to active neurons. However, it remains unclear which vessels mediate functional
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service