AMAB90865
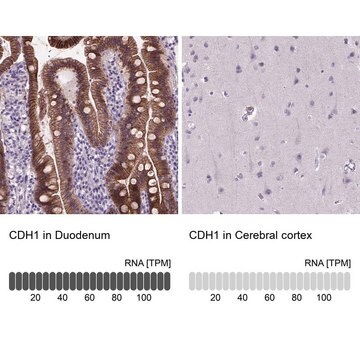
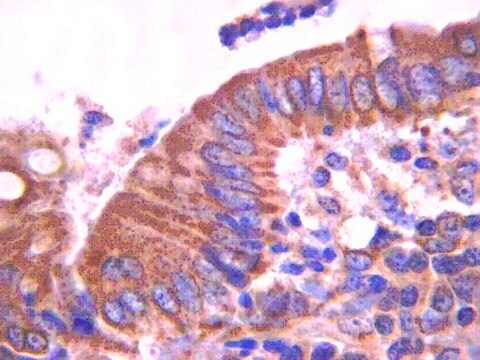
Monoclonal Anti-CDH1 antibody produced in mouse

Prestige Antibodies® Powered by Atlas Antibodies, clone CL1180, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-CD324, Anti-UVO, Anti-uvomorulin
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
biological source
mouse
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
CL1180, monoclonal
product line
Prestige Antibodies® Powered by Atlas Antibodies
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
species reactivity
human
enhanced validation
RNAi knockdown
orthogonal RNAseq
Learn more about Antibody Enhanced Validation
technique(s)
immunoblotting: 1 μg/mL
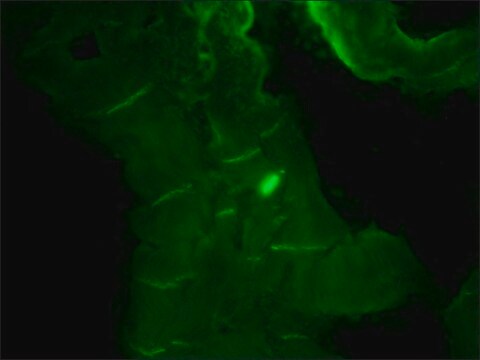
immunofluorescence: 2-10 μg/mL (Fixation/Permeabilization: PFA/Triton X-100)
immunohistochemistry: 1:1000- 1:2500
isotype
IgG2a
immunogen sequence
ATDNGSPVATGTGTLLLILSDVNDNAPIPEPRTIFFCERNPKPQVINIIDADLPPNTSPFTAELTHGASANWTIQYNDPTQESIILKPKMALEVGDYKINLKLMDNQNKDQVTTLEVSVCDCEGA
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... CDH1(999)
Immunogen
Application
The Human Protein Atlas project can be subdivided into three efforts: Human Tissue Atlas, Cancer Atlas, and Human Cell Atlas. The antibodies that have been generated in support of the Tissue and Cancer Atlas projects have been tested by immunohistochemistry against hundreds of normal and disease tissues and through the recent efforts of the Human Cell Atlas project, many have been characterized by immunofluorescence to map the human proteome not only at the tissue level but now at the subcellular level. These images and the collection of this vast data set can be viewed on the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) site by clicking on the Image Gallery link. We also provide Prestige Antibodies® protocols and other useful information.
Features and Benefits
Every Prestige Antibody is tested in the following ways:
- IHC tissue array of 44 normal human tissues and 20 of the most common cancer type tissues.
- Protein array of 364 human recombinant protein fragments.
Linkage
Physical form
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service