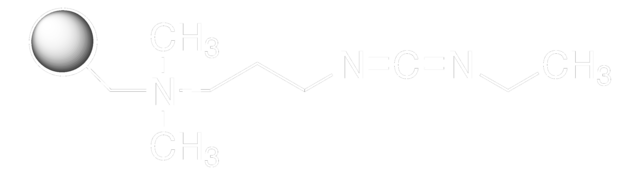
E1769
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
BioXtra
Synonym(s):
N-Ethyl-N′-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDAC, EDC, EDC hydrochloride, WSC hydrochloride
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, BioXtra
product line
BioXtra
Quality Level
form
powder
impurities
≤0.005% Phosphorus (P)
≤0.1% Insoluble matter
ign. residue
≤0.1%
mp
110-115 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: 0.5 M, clear to very slightly hazy, colorless to very faintly yellow
anion traces
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.05%
cation traces
Al: ≤0.0005%
Ca: ≤0.0005%
Cu: ≤0.0005%
Fe: ≤0.0005%
K: ≤0.005%
Mg: ≤0.0005%
NH4+: ≤0.05%
Na: ≤0.005%
Pb: ≤0.001%
Zn: ≤0.0005%
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H17N3.ClH/c1-4-9-8-10-6-5-7-11(2)3;/h4-7H2,1-3H3;1H
InChI key
FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- for post-fixation and crosslinking of small ribonucleic acid (RNAs) species from formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues, for fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH) and immunofluorescence (IF) signals
- for cross-linking of nanofiber matrices with mouse lung extract
- for activation of substrate XNA oligonucleotides
Biochem/physiol Actions
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Target Organs
Stomach,large intestine,lymph node
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Tissue engineering has become a key therapeutic tool in the treatment of damaged or diseased organs and tissues, such as blood vessels and urinary bladders.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service
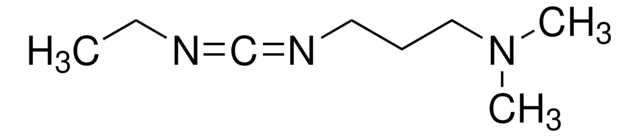







![1-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylcarbodiimide methiodide](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/414/134/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd/640/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd.png)