914088
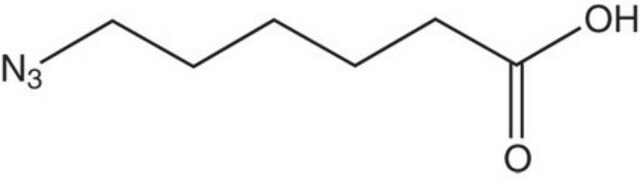
N6-((2-Azidoethoxy)carbonyl)-L-lysine hydrochloride
≥95%
Synonym(s):
(S)-2-amino-6-((2-azidoethoxy)carbonylamino)hexanoic acid hydrochloride, Clickable amino acid for bioconjugation, H-L-Lys(EO-N3)-OH HCl, Lysine-azide, UAA crosslinker
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95%
form
powder
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
[N+](=[N-])=NCCOC(=O)NCCCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O.C
InChI
1S/C9H17N5O4.CH4/c10-7(8(15)16)3-1-2-4-12-9(17)18-6-5-13-14-11;/h7H,1-6,10H2,(H,12,17)(H,15,16);1H4/t7-;/m0./s1
InChI key
LQERWAMRZNEGIE-FJXQXJEOSA-N
Application
Other Notes
Semisynthesis of an Active Enzyme by Quantitative Click Ligation
A Robust and Quantitative Reporter System To Evaluate Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation in Yeast
An orthogonalized platform for genetic code expansion in both bacteria and eukaryotes
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Self-react. C
Storage Class Code
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service