SAB4200147
Anti-FHOD1 antibody produced in rabbit
~1.0 mg/mL, affinity isolated antibody
Sinónimos:
Anti-FH1/FH2 domain-containing protein 1, Anti-FHOS, Anti-Formin homology-2 domain-containing protein 1, Anti-formin homolog overexpressed in spleen 1, Anti-formin homology 2 domain-containing protein 1
About This Item
WB
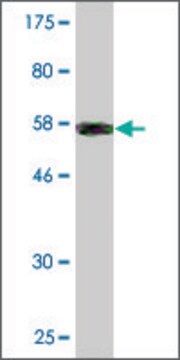
western blot: 0.5-1.0 μg/mL using whole extracts of human K562 cells
Productos recomendados
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
~130 kDa
species reactivity
human
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μL
concentration
~1.0 mg/mL
technique(s)
immunohistochemistry: 10-20 μg/mL using heat-retrieved formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human spleen sections and biotin, ExtrAvidin® peroxidase staining system
western blot: 0.5-1.0 μg/mL using whole extracts of human K562 cells
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... FHOD1(29109)
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Legal Information
Disclaimer
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico