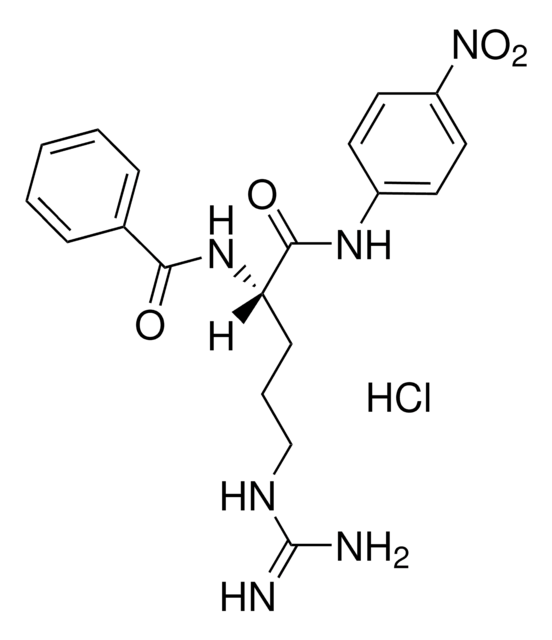
70124
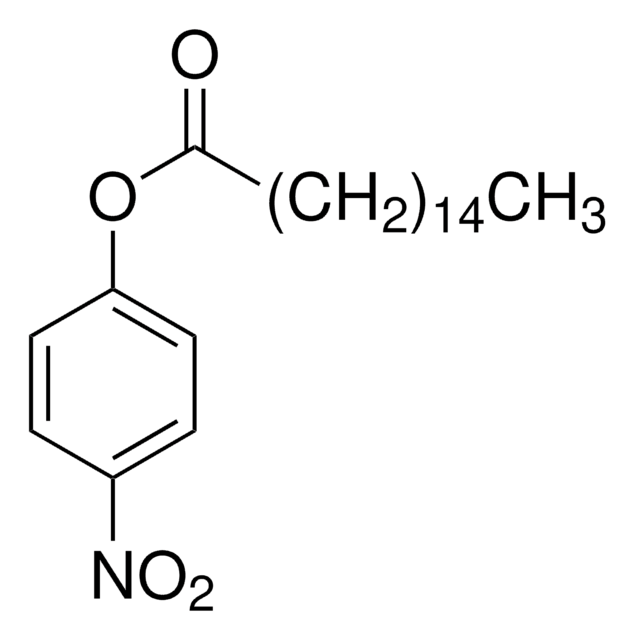
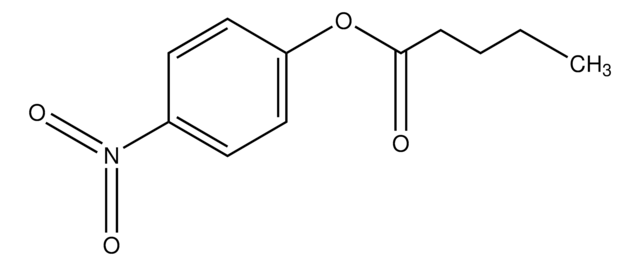
4-Nitrophenyl myristate
lipase substrate, ≥95.0% (HPLC), powder
Sinónimos:
4-Nitrophenyl tetradecanoate
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C20H31NO4
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
349.46
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
2004374
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.83
Productos recomendados
Nombre del producto
4-Nitrophenyl myristate, ≥95.0% (HPLC)
Quality Level
assay
≥95.0% (HPLC)
form
powder
solubility
chloroform: 50 mg/mL, clear to very slightly hazy, colorless to dark yellow
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)Oc1ccc(cc1)[N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C20H31NO4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-20(22)25-19-16-14-18(15-17-19)21(23)24/h14-17H,2-13H2,1H3
InChI key
ZBBNFJIVAHGZKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
4-Nitrophenyl myristate has been used as a substrate to measure the activity of:
- bile salt-activated lipase
- esterase
- neutral lipase
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Qiaoqiao Sun et al.
Journal of bioscience and bioengineering, 122(5), 539-544 (2016-10-26)
Thermophilic Neosartorya fischeri P1 is an excellent lipase producer and harbors seven lipase genes. All genes were found to be functional after heterologous expression in Escherichia coli. One of them, LIP09, showed high-level expression in Pichia pastoris with the yield
Mirella Vazzana et al.
The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 147(4), 2414-2414 (2020-05-04)
Underwater sounds generated by anthropogenic activity can cause behavior changes, temporary loss of hearing, damage to parts of the body, or death in a number of marine organisms and can also affect healing and survival. In this study, the authors
Maria Stella Cappello et al.
Systematic and applied microbiology, 33(8), 461-467 (2010-11-26)
The diversity of indigenous Oenococcus oeni strains was investigated by molecular and biochemical characterization of isolates from Malvasia Nera wine, an economically important red wine of the Salento Region (Apulia, Italy), during spontaneous malolactic fermentation (MLF). A total of 82
Héctor Cordero et al.
Fish & shellfish immunology, 58, 500-507 (2016-10-23)
Skin mucus is increasingly used as a source for determining immunity-related proteins and enzymes. However, the ability to accurately measure some activities may be modified by inadequate handling and storage of the samples. This study aims to measure the effect
Israel García-Cano et al.
Journal of dairy science, 103(5), 3912-3923 (2020-03-10)
Lipolysis occurs during ripening of dairy products as a result of esterase or lipase activity. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are considered to be weakly lipolytic bacteria compared with other species. In cheeses with extended ripening periods, lipolytic LAB may have
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico