A0701
Agarosa, baja temperatura de gelificación
Type VII-A
Sinónimos:
2-hidroxietil agarosa
About This Item
Productos recomendados
type
Type VII-A
Quality Level
form
powder
technique(s)
electrophoresis: suitable
impurities
≤7% water
ash
≤0.4%
turbidity
≤4 NTU (1.5% gel)
EEO
≤0.12
mp
65 °C±1 °C
transition temp
gel point 26 °C ±2 °C (1.5% gel)
gel strength
≥250 g/cm2 (1% gel)
anion traces
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.4%
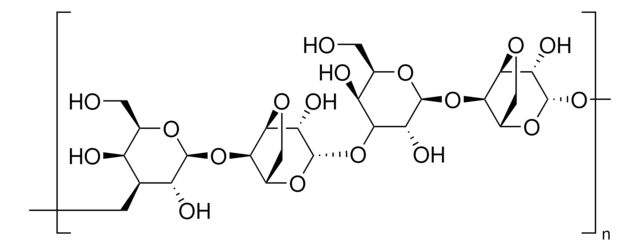
SMILES string
O1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@H]1CO)O)O[C@@H]4O[C@@H]5[C@H]([C@@H](OC5)[C@@H]4O)O[C@@H]6O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]6O)O)O)CO)O)O[C@H]2[C@H]3OC[C@@H]2O[C@H]([C@H]3O)O
InChI
1S/C24H38O19/c25-1-5-9(27)11(29)12(30)22(38-5)41-17-8-4-36-20(17)15(33)24(40-8)43-18-10(28)6(2-26)39-23(14(18)32)42-16-7-3-35-19(16)13(31)21(34)37-7/h5-34H,1-4H2/t5-,6-,7+,8+,9+,10+,11+,12-,13+,14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20+,21-,22+,23+,24+/m1/s1
InChI key
MJQHZNBUODTQTK-WKGBVCLCSA-N
Categorías relacionadas
General description
Application
Agarose has been used:
- to encapsulate Escherichia coli on a hydrogel in tissue culture
- to entrap Aliivibrio fischeri on a disposable card involved in designing of toxicity biosensors
- as a the dispersed phase of emulsion during preparation agar beads
Biochem/physiol Actions
Analysis Note
Contenido de sulfatos - utilizados como un indicador de pureza, ya que los sulfatos constituyen el principal grupo iónico presente.
Fuerza del gel - la fuerza que debe aplicarse a un gel para provocar su fractura.
Punto de gelificación - la temperatura a la cual una disolución acuosa de agarosa forma un gel cuando se enfría. Las disoluciones de agarosa exhiben histéresis en la transición de líquido a gel - es decir, su punto de gelificación no es el mismo que su temperatura de fusión.
Electroendosmosis (EEO) - movimiento de líquido a través del gel. En un gel de agarosa, los grupos aniónicos están pegados a la matriz y no pueden moverse, pero los contra-cationes disociables pueden migrar en la matriz hacia el cátodo, dando lugar a EEO. Dado que el movimiento electroforético de los biopolímeros suele ser en dirección al ánodo, la EEO puede alterar las separaciones debido a la convección interna.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico