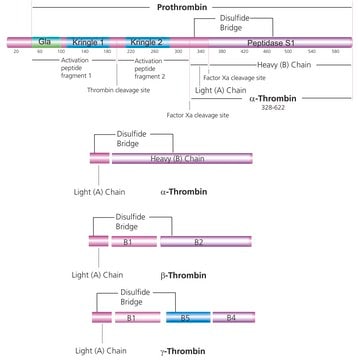
ABE1865
Anti-UTX (KDM6A)
from rabbit, purified by affinity chromatography
Sinónimos:
Lysine-specific demethylase 6A, Histone demethylase UTX, Ubiquitously-transcribed TPR protein on the X chromosome, Ubiquitously-transcribed X chromosome tetratricopeptide repeat protein
About This Item
Productos recomendados
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
purified by
affinity chromatography
species reactivity
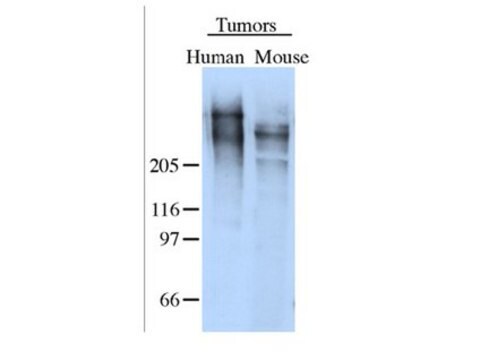
human, mouse
technique(s)
ChIP: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
ambient
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... KDM6A(7403)
General description
Ref.:
Lederer, D et al. (2012). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 90, 119-124.
Zha, L et al. (2015). J. Biol. Chem. 290, 25151-25163.
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Analysis: A representative lot detected a time-dependent UTX (KDM6A) enrichement at the Myogenin and CKm regulatory regions following myogenic differentiation of murine C2C12 myoblasts. shRNA-mediated Six4 knockdown, but not p38 MAPK inhibition, downregulated UTX (KDM6A) recruitment to the Myogenin and CKm loci (Seenundun, S., et al. (2010). EMBO J. 29(8):1401-1411).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected UTX (KDM6A) immunoreactivity by indirect immunofluorescence staining of 1% paraformaldehyde-fixed, 0.5% Triton X-100-permeabilized myofibers isolated from mouse extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles (Faralli, H., et al. (2016). J. Clin. Invest. 126(4):1555-1565).
Immunofluorescence Analysis: A representative lot detected UTX (KDM6A) immunoreactivity by indirect immunofluorescence staining of 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed, 1% Triton X-100-permeabilized, transverse OCT cryosections sections of mouse tibialis anterior skeletal muscle (Faralli, H., et al. (2016). J. Clin. Invest. 126(4):1555-1565).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot co-immunoprecipitated PTIP and RbBP5 with UTX using embryonic stem cell (ESC) nuclear extracts from wild-type or Utx(KI/KI) mice harboring homozygous demethylase dead Utx mutant gene knock-in. No UTX/PTIP/RbBP5 complex was precipitated from Utx-knockout ESCs (Faralli, H., et al. (2016). J. Clin. Invest. 126(4):1555-1565).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot co-immunoprecipitated Six4 with UTX (KDM6A) using nuclear extract from murine C2C12 myoblasts 24 hrs post myogenic differentiation (Seenundun, S., et al. (2010). EMBO J. 29(8):1401-1411).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected UTX4 in myoblast whole cell lysates and embryonic stem cell (ESC) nuclear extracts from wild-type or Utx(KI/KI) mice harboring homozygous demethylase dead Utx mutant gene knock-in, as well as in UTX and MLL4 immunoprecipitates. No UTX target band was detected in Utx-knockout ESCs (Faralli, H., et al. (2016). J. Clin. Invest. 126(4):1555-1565).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected UTX (KDM6A) in nuclear extracts from human K562 and murine C2C12 myoblasts (24 hrs post myogenic differentiation), as well as in Six4 immunoprecipitates. shRNA treatment prior to nuclear extract preparation diminished target band detection (Seenundun, S., et al. (2010). EMBO J. 29(8):1401-1411).
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Quality
Western Blotting Analysis: 0.2 µg/mL of this antibody detected UTX (KDM6A) in 10 µg of HeLa nuclear extract.
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Other Notes
Disclaimer
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico