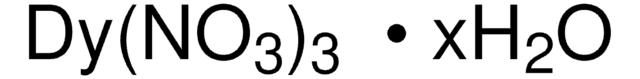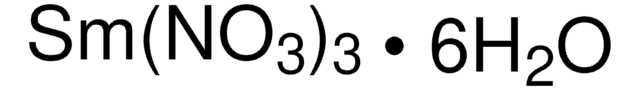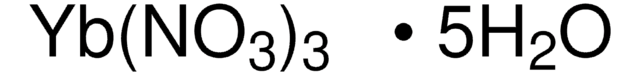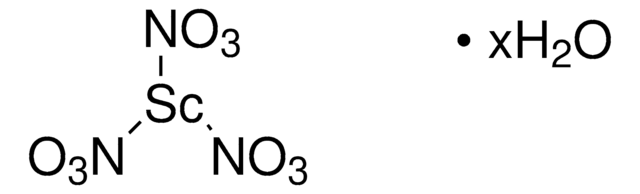930911
Praseodymium nitrate hexahydrate
99.99% (trace rare earth metals basis)
Sinónimos:
Praseodymium(III) nitrate hexahydrate, Nitric acid praseodymium(3+) salt, Praseodymium trinitrate, Praseodymium trinitrate hexahydrate
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Quality Level
assay
99.99% (trace rare earth metals basis)
form
crystals
impurities
≤150 ppmtrace (rare earth metals)
≤500 ppm (trace metals)
mp
<100 °C ((lit.))
solubility
H2O: soluble ((lit.))
density
2.233 g/cm3 ((lit.))
SMILES string
O.O.O.O.O.O.[Pr+3].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/3NO3.6H2O.Pr/c3*2-1(3)4;;;;;;;/h;;;6*1H2;/q3*-1;;;;;;;+3
InChI key
LXXCECZPOWZKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Application
Related product
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Ox. Sol. 3 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class
5.1B - Oxidizing hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 2
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Lo sentimos, en este momento no disponemos de COAs para este producto en línea.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico