914088
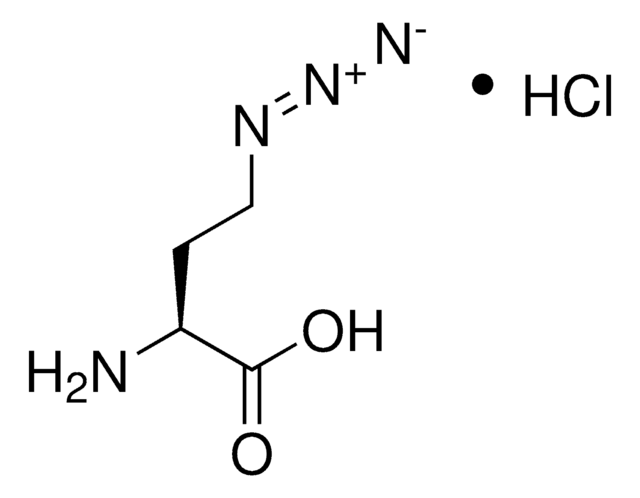
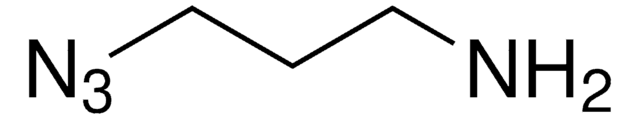
N6-((2-Azidoethoxy)carbonyl)-L-lysine hydrochloride
≥95%
Sinónimos:
(S)-2-amino-6-((2-azidoethoxy)carbonylamino)hexanoic acid hydrochloride, Clickable amino acid for bioconjugation, H-L-Lys(EO-N3)-OH HCl, Lysine-azide, UAA crosslinker
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Application
Other Notes
Semisynthesis of an Active Enzyme by Quantitative Click Ligation
A Robust and Quantitative Reporter System To Evaluate Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation in Yeast
An orthogonalized platform for genetic code expansion in both bacteria and eukaryotes
Related product
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Self-react. C
Storage Class
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Lo sentimos, en este momento no disponemos de COAs para este producto en línea.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico