764914
Poly(ethylene glycol) 4-cyano-4-(phenylcarbonothioylthio)pentanoate
average Mn 2,000
Sinónimos:
PEG CTA, PEG RAFT
About This Item
Productos recomendados
description
PEG average Mn 2,000 n~44
form
powder
mol wt
average Mn 2,000
mp
47-52 °C
PDI
≤1.1
storage temp.
2-8°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Application
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Artículos
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization is rapidly moving to the forefront in construction of drug and gene delivery vehicles.
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
Humankind has utilized protein materials throughout its existence, starting with the use of materials such as wool and silk for warmth and protection from the elements and continuing with the use of recombinant DNA techniques to synthesize proteins with unique and useful properties.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico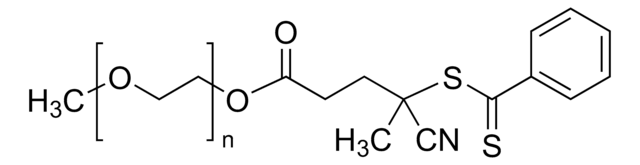
![Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether 4-cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoate average Mn 10,000](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/618/250/98532519-ae4b-4fc4-b6f0-fb15f144c8f1/640/98532519-ae4b-4fc4-b6f0-fb15f144c8f1.png)
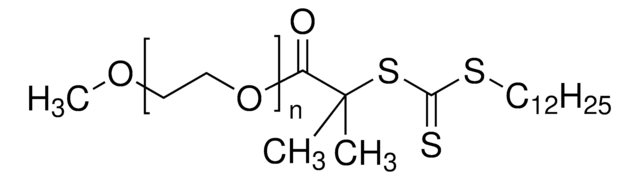
![Poly(ethylene glycol) bis[2-(dodecylthiocarbonothioylthio)-2-methylpropionate] average Mn 10,800](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/369/930/ba9a86e7-8635-4a23-aa7c-7db94c295272/640/ba9a86e7-8635-4a23-aa7c-7db94c295272.png)

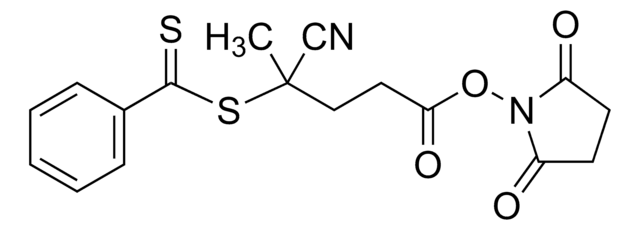
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)