推薦產品
生物源
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
品質等級
化驗
≥98.5% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
光學活性
[α]/D 174 to 182 °, c = 1.0% (w/v) in water
技術
HPLC: suitable
cryopreservation: suitable
mp
97-99 °C
應用
agriculture
agriculture
cell analysis
genomic analysis
life science and biopharma
SMILES 字串
[H]O[H].[H]O[H].OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O
InChI
1S/C12H22O11.2H2O/c13-1-3-5(15)7(17)9(19)11(21-3)23-12-10(20)8(18)6(16)4(2-14)22-12;;/h3-20H,1-2H2;2*1H2/t3-,4-,5-,6-,7+,8+,9-,10-,11-,12-;;/m1../s1
InChI 密鑰
DPVHGFAJLZWDOC-PVXXTIHASA-N
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
相關類別
一般說明
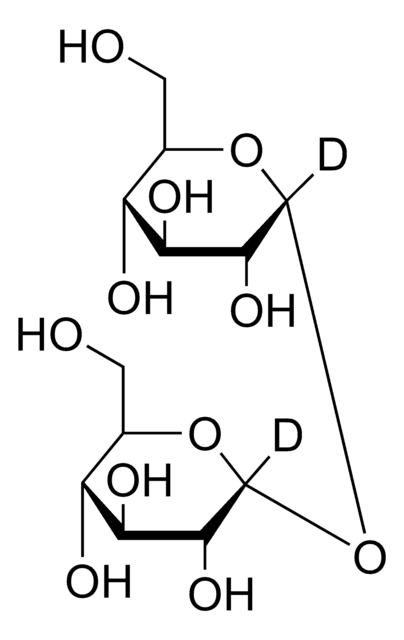
D-(+)-海藻糖是一种二糖,作为化学伴侣并作为微生物中的碳水化合物储备。它起到渗透调节剂的作用,保护细胞免受各种环境压力的影响。此外,它还在冷冻干燥过程中的蛋白质稳定性方面发挥着至关重要的作用,使其成为生化、细胞培养和赋形剂研究领域的宝贵资产
應用
- 在各种细胞冷冻介质中用作冷冻保护剂
- 用于赋形剂研究
生化/生理作用
海藻糖是一种由两个葡萄糖单位通过1-1α键结合而形成的非还原性糖。它被认为可为植物和动物提供承受缺水阶段的能力。
特點和優勢
- 由酿酒酵母制备
- 适用于 HPLC 和 GC-MS(4)
準備報告
由Payen, R., Can的修改过程而制备。J. Res., 27B, 749 (1949).
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
Sandra Jesus et al.
AAPS PharmSciTech, 19(1), 101-113 (2017-06-15)
This report extensively explores the benefits of including chitosan into poly-ε-caprolactone (PCL) nanoparticles (NPs) to obtain an improved protein/antigen delivery system. Blend NPs (PCL/chitosan NPs) showed improved protein adsorption efficacy (84%) in low shear stress and aqueous environment, suggesting that
Alan Twomey et al.
International journal of pharmaceutics, 487(1-2), 91-100 (2015-04-19)
In frozen and lyophilized systems, the biological to be stabilized (e.g. therapeutic protein, biomarker, drug-delivery vesicle) and the cryo-/lyo-protectant should be co-localized for successful stabilization. During freezing and drying, many factors cause physical separation of the biological from the cryo-/lyo-protectant
Sabine Ullrich et al.
Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 104(6), 2040-2046 (2015-04-03)
The importance of cake adhesion to the inside vial wall during lyophilization of amorphous trehalose cakes was determined by using hydrophobized vials. The degrees of cake shrinkage and cracking were determined independently by photographic imaging of the cake top surface
Joachim Schaefer et al.
International journal of pharmaceutics, 489(1-2), 124-130 (2015-05-06)
The inactivation of catalase during spray-drying over a range of outlet gas temperatures could be closely represented by the Arrhenius equation. From this an activation energy for damage to the catalase could be calculated. The close fit to Arrhenius suggests
Anke Sass et al.
Drug development and industrial pharmacy, 40(6), 749-757 (2013-04-20)
The spray-drying behaviour of 16 water-miscible organic solvents on a bench-scale machine (Büchi B290 with inert loop) was determined under mild-to-moderate process conditions, namely inlet gas temperature of 130 °C and liquid feed flow rate of ≤3 mL/min. The solvents with boiling
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務