推薦產品
一般說明
MYC oncogene is a global transcription factor. The gene is located on human chromosome 8q24.21. MYC oncogene is a cancer promoting gene.
生化/生理作用
C-myc oncogene has high proliferative capacity. Overexpression of this gene is associated with Burkitt lymphoma. C-myc oncogene is implicated in various malignant tumors, such as, leukemia, lymphoma and human solid tumor.
The universal deregulation of c-Myc gene expression in tumor cells suggests that this oncogene represents an attractive target for cancer therapeutic purposes. The c-Myc promoter integrates diverse mitogenic signaling cascades, which are constitutively activated in tumor cells, and translates them into expression of the c-Myc transcription factor, which promotes cell proliferation, growth, differentiation, and apoptosis by regulating the expression of numerous target genes. The structural and biochemical features of the MYC family (MYC, N-MYC, and L-MYC) mark them as direct regulators of gene expression. As basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper proteins (bHLH-ZIP), the MYCs acquire the capacity to bind the DNA sequence CACGTG (E-box) when dimerized with MAX (another bHLH-ZIP, 4,5). A head-to-tail pair of MYC-MAX dimers may, in turn, form a heterotetramer capable of bridging distant E-boxes. Among the broadly distributed positive enforcers of MYC action that are often recruited to target genes are chromatin remodeling (SWI/SNF relatives) and modifying complexes (TRAPP/GCN5 and relatives); these complexes mobilize nucleosomes and acetylate histones and/or other targets to activate gene expression. MYC binds TBP along an auxiliary pathway to control gene expression. MAD and MNT generally oppose MYC action by enlisting histone deacetylase complexes. Besides acting at the level of chromatin, MYC may also operate at later stages of the transcription cycle, after pre-initiation complex formation. In addition to using generic chromatin complexes to up- or down-regulate transcription, the MYC network also conscripts individual factors to modify expression locally on an ad hoc basis. For example, YY1, AP2, MIZ1, SP1, BRCA1, and other proteins interact directly with MYC, and so may directly modify the output of the MYC network.
外觀
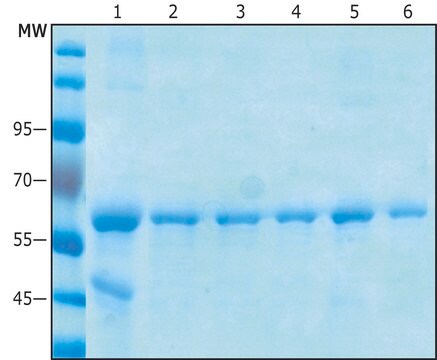
Clear and colorless frozen liquid solution
準備報告
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. While working, please keep sample on ice.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
C V Dang et al.
Experimental cell research, 253(1), 63-77 (1999-12-02)
The c-myc gene and the expression of the c-Myc protein are frequently altered in human cancers. The c-myc gene encodes the transcription factor c-Myc, which heterodimerizes with a partner protein, termed Max, to regulate gene expression. Max also heterodimerizes with
Deconstructing myc.
R N Eisenman
Genes & development, 15(16), 2023-2030 (2001-08-21)
Consistent MYC and FLT4 gene amplification in radiation-induced angiosarcoma but not in other radiation-associated atypical vascular lesions
Guo T, et al.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 50(1), 25-33 (2011)
Low expression of c-Myc protein predicts poor outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after resection
Ji F, et al.
BMC Cancer, 18(1), 460-460 (2018)
Novel synthetic 4-chlorobenzoyl berbamine inhibits c-Myc expression and induces apoptosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells
Zhang L, et al.
Annals of Hematology, 97(12), 2353-2362 (2018)
文章
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about how proliferating cells require the biosynthesis of structural components for biomass production and for genomic replication.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務