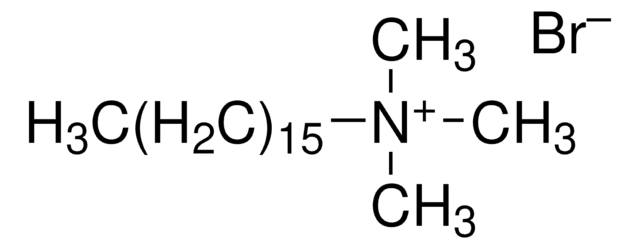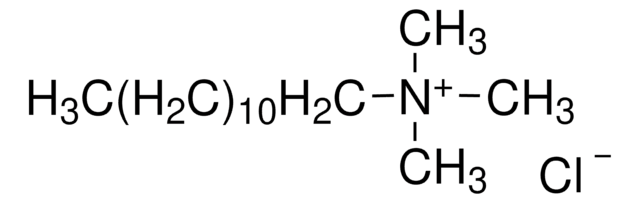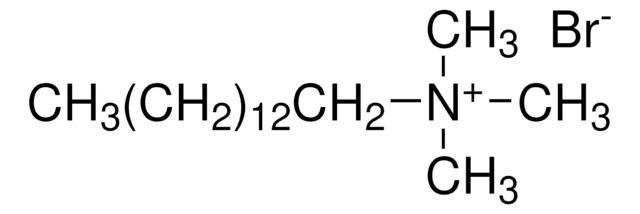推薦產品
生物源
synthetic (oragnic)
品質等級
描述
cationic
化驗
≥98%
形狀
powder
分子量
308.34 g/mol
mp
246 °C (dec.) (lit.)
溶解度
954 g/L at 20 °C
密度
1.17 g/cm3 at 20 °C (68 °F)
SMILES 字串
[Br-].CCCCCCCCCCCC[N+](C)(C)C
InChI
1S/C15H34N.BrH/c1-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16(2,3)4;/h5-15H2,1-4H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
InChI 密鑰
XJWSAJYUBXQQDR-UHFFFAOYSA-M
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
十二烷基三甲基溴化铵 (DTAB) 是一种多功能季铵表面活性剂,在细胞生物学和生化研究中具有广泛的应用。其独特的特性使其成为溶解蛋白质和肽、提取 DNA 和裂解细胞的宝贵工具。在蛋白质组学研究中,DTAB 在蛋白质溶解和纯化中发挥着至关重要的作用。它破坏疏水相互作用和静电力的能力使其能够有效溶解膜结合蛋白和肽,使它们易于分析和表征。这一特性在涉及膜蛋白的蛋白质组学研究中尤其重要,而膜蛋白通常难以使用传统方法溶解。
除了蛋白质溶解之外,这种阳离子去污剂还可以应用于 DNA 提取过程。它能够与 DNA 相互作用并改变其构象,从而促进 DNA 从细胞成分中释放,从而实现后续的纯化和分析。这一特性对于从各种生物样品(包括组织、细胞和微生物)中分离 DNA 来说特别有用。此外,DTAB 在细胞裂解过程中表现出有效性。它破坏细胞膜并释放细胞内成分的能力使其成为分解细胞并获取细胞内容物的宝贵工具。该特性在各种生物学研究中都有应用,包括蛋白质提取、酶测定和细胞成分分析。
十二烷基三甲基溴化铵 (DTAB) 是一种多功能且应用广泛的表面活性剂,在蛋白质组学研究、细胞生物学和生化研究中具有多种应用 。它溶解蛋白质和肽、提取 DNA 和裂解细胞的能力使其成为各种生物研究和分析技术的重要工具。
除了蛋白质溶解之外,这种阳离子去污剂还可以应用于 DNA 提取过程。它能够与 DNA 相互作用并改变其构象,从而促进 DNA 从细胞成分中释放,从而实现后续的纯化和分析。这一特性对于从各种生物样品(包括组织、细胞和微生物)中分离 DNA 来说特别有用。此外,DTAB 在细胞裂解过程中表现出有效性。它破坏细胞膜并释放细胞内成分的能力使其成为分解细胞并获取细胞内容物的宝贵工具。该特性在各种生物学研究中都有应用,包括蛋白质提取、酶测定和细胞成分分析。
十二烷基三甲基溴化铵 (DTAB) 是一种多功能且应用广泛的表面活性剂,在蛋白质组学研究、细胞生物学和生化研究中具有多种应用 。它溶解蛋白质和肽、提取 DNA 和裂解细胞的能力使其成为各种生物研究和分析技术的重要工具。
應用
十二烷基三甲基溴化铵已用于裂解新生儿正常人表皮角质化细胞(NHEK),以量化细胞内烟酰胺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸(NADP+)和NADPH(简化型)的含量。
十二烷基三甲基溴化铵已用于评估二元混合抗衡离子在表面活性剂吸附膜中的分布。它也被用于研究萃取有机磷农药的表面活性剂的链长相容性。
特點和優勢
适用于细胞生物学和生化研究的高品质化合物
同類產品
產品號碼
描述
訂價
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
儲存類別代碼
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
客戶也查看了
Study on the distribution of binary mixed counterions in surfactant adsorbed films by total reflection XAFS measurements
Y Imai et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 15, 219-224 (2012)
Annabell Plauth et al.
Free radical biology & medicine, 99, 608-622 (2016-10-23)
Resveratrol has gained tremendous interest owing to multiple reported health-beneficial effects. However, the underlying key mechanism of action of this natural product remained largely controversial. Here, we demonstrate that under physiologically relevant conditions major biological effects of resveratrol can be
Xiaofeng Chang et al.
Journal of colloid and interface science, 377(1), 291-298 (2012-04-28)
This study reported, for the first time systematically, photodegradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) in aqueous solution over BiOCl and BiOBr semiconductors. Under visible light irradiation (λ>400 nm, λ>420 nm and λ=550±15 nm), RhB adsorbed on the surface of BiOCl and
Jonas Carlstedt et al.
Physical chemistry chemical physics : PCCP, 14(27), 9574-9577 (2012-06-14)
Polyelectrolytes with amphiphilic counterions, PEACs, are water insoluble because the amphiphiles self-assemble into highly charged micelles that strongly associate with the equally highly charged polyions. However, in the presence of water soluble cyclodextrins (CDs) that form inclusion complexes with the
Ye Liu et al.
Lab on a chip, 12(19), 3746-3753 (2012-07-31)
Although biochemical sensing using liquid crystals (LC) has been demonstrated, relatively little attention has been paid towards the fabrication of in situ-formed LC sensing devices. Herein, we demonstrate a highly reproducible method to create uniform LC thin film on treated
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務