推薦產品
描述
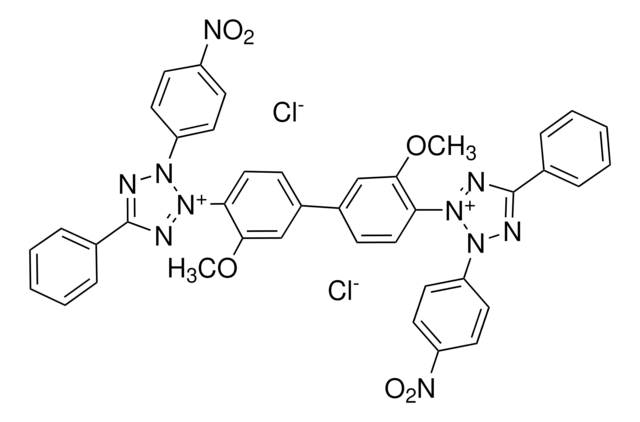
4-Nitro blue tetrazolium chloride, crystals
品質等級
形狀
crystals
包裝
pkg of 5 g
製造商/商標名
Roche
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
[Cl-].[Cl-].COc1cc(ccc1-[n+]2nc(nn2-c3ccc(cc3)[N+]([O-])=O)-c4ccccc4)-c5ccc(c(OC)c5)-[n+]6nc(nn6-c7ccc(cc7)[N+]([O-])=O)-c8ccccc8
InChI
1S/C40H30N10O6.2ClH/c1-55-37-25-29(13-23-35(37)47-43-39(27-9-5-3-6-10-27)41-45(47)31-15-19-33(20-16-31)49(51)52)30-14-24-36(38(26-30)56-2)48-44-40(28-11-7-4-8-12-28)42-46(48)32-17-21-34(22-18-32)50(53)54;;/h3-26H,1-2H3;2*1H/q+2;;/p-2
InChI 密鑰
FSVCQIDHPKZJSO-UHFFFAOYSA-L
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
NBT可溶于水、水性缓冲液和二甲基甲酰胺。
四唑盐可用于测定多种来源细胞的代谢活性。含有四个氮原子的四元四唑环核心具有净正电荷,通过膜电位诱导细胞摄取。这推动了它在细胞生物学领域的应用。在免疫标记技术中,硝基蓝四氮唑(NBT)可用作氧化剂。 碱性磷酸酶水解5-溴-4-氯-3-吲哚磷酸酯(BCIP)产生靛白,然后被NBT还原,形成不溶性蓝色BCI。NBT是一种无色/黄色染料,可被某些细胞还原而产生蓝色或黑色甲臜晶体。NBT的这种性质使其成为氧化还原组织化学和生物化学应用的首选染料。它曾被用于区分非细菌性和细菌性疾病,其中,细菌性疾病可导致中性粒细胞还原染料;用于确诊慢性肉芽肿病。
應用
- 菌落和噬菌斑杂交
- 免疫组织细胞化学
- 原位 杂交
- Northern印迹
- Southern印迹
- 蛋白质免疫印迹
NBT已可用于 原位 杂交。
準備報告
工作溶液:溶解度: 溶于水、水性缓冲液和二甲基甲酰胺。可溶于甲醇。可得到浓度为20 mg/ml的澄清溶液。
分析報告
吸光度: NBT 在260 nm[溶剂为水]具有最大吸光度,
终产物甲臜在605 nm[溶剂为硝基苯]中具有最大吸光度。
终产物甲臜在605 nm[溶剂为硝基苯]中具有最大吸光度。
Performance-controlled in the LDH assay.
其他說明
仅用于生命科学研究。不可用于诊断。
訊號詞
Warning
危險分類
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
標靶器官
Respiratory system
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
does not flash
閃點(°C)
does not flash
客戶也查看了
D Liebhart et al.
Journal of comparative pathology, 135(4), 237-242 (2006-10-31)
For use in an in-situ hybridization method, three probes (HM, TR and BL) were designed to hybridize, respectively, with (1) Histomonas meleagridis, (2) Tetratrichomonas gallinarum, and (3) a broad range of micro-organisms, including Blastocystis spp. Mono-eukaryotic cultures were used to
Infection and nitroblue-tetrazolium reduction by neutrophils: A diagnostic aid.
Park B H, et al.
Lancet, 292(7567), 532-534 (1968)
Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: new insights into their cellular reduction.
Berridge M V, et al.
Biotechnology Annual Review, 11, 127-152 (2005)
Fluorescent in situ hybridization employing the conventional NBT/BCIP chromogenic stain.
Trinh L A, et al.
Biotechniques, 42(6), 756-759 (2007)
Wanlong Su et al.
Frontiers in plant science, 11, 568411-568411 (2021-02-09)
Salt stress is an adverse environmental factor for plant growth and development. Under salt stress, plants can activate the selective autophagy pathway to alleviate stress. However, the regulatory mechanism of selective autophagy in response to salt stress remains largely unclear.
條款
NBT Protocol
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務