5.09584
ISR Inhibitor, ISRIB
同義詞:
ISR Inhibitor, ISRIB, trans-2-(4-Chlorophenoxy)-N-(4-(2-(4-chlorophenoxy)acetylamino)cyclohexyl)acetamide, Integrated Stress Response Inhibitor, UPR Inhibitor, eIF2α (pS51) Signaling Inhibitor, eIF2S1 (pS51) Signaling Inhibitor, eIF2α (pS51) Signaling Inhibitor, eIF2S1 (pS51) Signaling Inhibitor, trans-2-(4-Chlorophenoxy)-N-(4-(2-(4-chlorophenoxy)acetylamino)cyclohexyl)acetamide, Integrated Stress Response Inhibitor, UPR Inhibitor
About This Item
推薦產品
化驗
≥93% (HPLC)
品質等級
形狀
powder
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
protect from light
顏色
light beige
溶解度
DMSO: 10 mg/mL
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
C1CC(CCC1NC(=O)COC2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)NC(=O)COC3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl
InChI
1S/C22H24Cl2N2O4/c23-15-1-9-19(10-2-15)29-13-21(27)25-17-5-7-18(8-6-17)26-22(28)14-30-20-11-3-16(24)4-12-20/h1-4,9-12,17-18H,5-8,13-14H2,(H,25,27)(H,26,28)
InChI 密鑰
HJGMCDHQPXTGAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
一般說明
生化/生理作用
包裝
警告
重構
其他說明
法律資訊
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務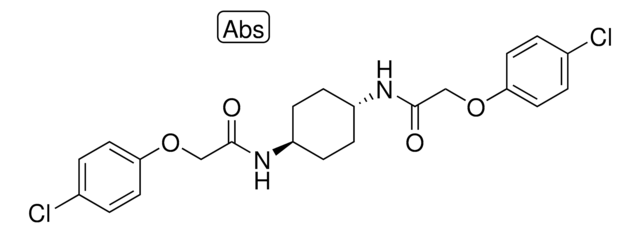

![PERK抑制剂I,GSK2606414 GSK2606414 is a cell-permeable, highly potent inhibitor of EIF2AK3/PERK (IC₅₀ = 0.4 nM; [ATP] = 5 µM). Targets PERK in its inactive DFG conformation at the ATP-binding region.](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/180/559/efa716dc-d5fe-4339-a6f0-0103084fc04a/640/efa716dc-d5fe-4339-a6f0-0103084fc04a.png)