推薦產品
product name
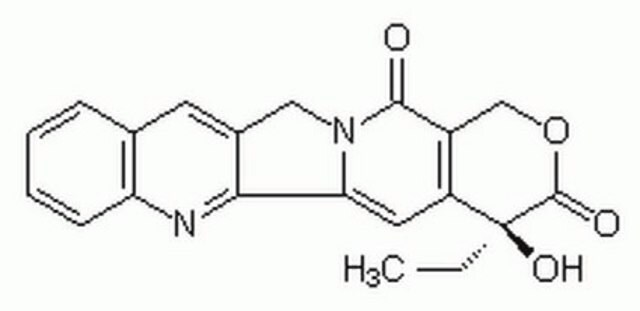
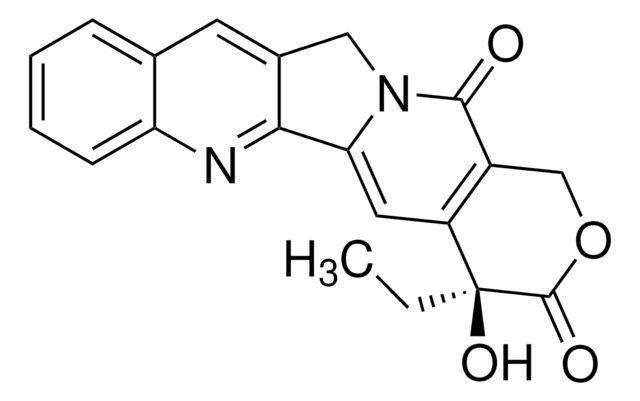
依托泊苷, A cell-permeable derivative of podophyllotoxin that acts as a topoisomerase II inhibitor (IC₅₀ = 59.2 µM) has major activity against a number of tumors, including germ cell neoplasms, small cell lung cancer, and malignant lymphoma.
品質等級
化驗
≥95% (HPLC)
形狀
solid
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
protect from light
顏色
white
溶解度
DMSO: 25 mg/mL
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
10-30°C
InChI
1S/C29H32O13/c1-11-36-9-20-27(40-11)24(31)25(32)29(41-20)42-26-14-7-17-16(38-10-39-17)6-13(14)21(22-15(26)8-37-28(22)33)12-4-18(34-2)23(30)19(5-12)35-3/h4-7,11,15,20-22,24-27,29-32H,8-10H2,1-3H3/t11-,15+,20-,21-,22+,24-,25-,26-,27-,29+/m1/s1
InChI 密鑰
VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-MRVIYFEKSA-N
一般說明
生化/生理作用
拓扑异构酶2
警告
重構
其他說明
Kaufman, S.H., et al. 1993.Cancer Res.53, 3976.
Onishi, Y., et al. 1993.Biochim.Biophys.Acta1175, 147.
Terada, T., et al. 1993.J. Med. Chem. 36, 1689.
Wazniak, A.J., et al. 1991.J. Clin. Oncol.9, 70.
Einhorn, L.H., et al. 1988.J. Clin. Oncol.6, 451.
Issel, B.F.1982.Cancer Chemother.Pharmacol.7, 73.
法律資訊
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Carc. 1B - Repr. 2
儲存類別代碼
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務