930512
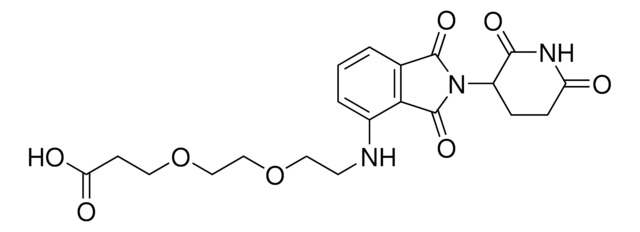
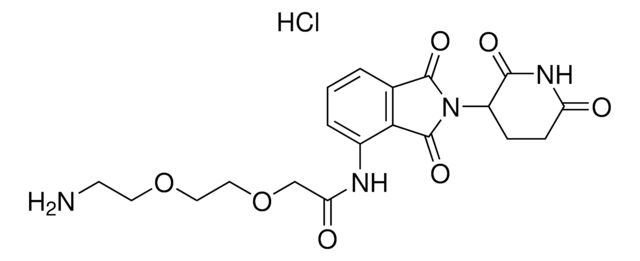
VH 032 amide-PEG3-acid
≥95.0%
同義詞:
(S, R, S)-AHPC-PEG3-acid, 3-Dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamoyl}ethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy}propanoic acid, 3-{2 -[2-(2-{[(2S)-1-[(2S,4R)-4-Hydroxy-2-({[4-(4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)phenyl]methyl}carbamoyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3, N-[3-[2-[2-(2-Carboxyethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy]-1-oxopropyl]-3-methyl-L-valyl-4-hydroxy-N-[[4-(4-methyl-5-thiazolyl)phenyl]methyl]-, L-Prolinamide
登入查看組織和合約定價
全部照片(1)
About This Item
推薦產品
ligand
VH032
品質等級
化驗
≥95.0%
形狀
powder
官能基
carboxylic acid
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
OC(CCOCCOCCOCCC(N[C@@H](C(C)(C)C)C(N1[C@@H](C[C@H](C1)O)C(NCC2=CC=C(C3=C(N=CS3)C)C=C2)=O)=O)=O)=O
應用
VH 032 amide-PEG3-acid is a functionalized von-Hippel-Lindau (VHL) ligand with a terminal carboxyl group, allowing rapid conjugation of amine containing linkers. A basic building block for development of a protein degrader library.
Technology Spotlight: Degrader Building Blocks for Targeted Protein Degradation
Protein Degrader Building Blocks
Automate your VHL-PEG based PROTACs with Synple Automated Synthesis Platform (SYNPLE-SC002)
Technology Spotlight: Degrader Building Blocks for Targeted Protein Degradation
Protein Degrader Building Blocks
Automate your VHL-PEG based PROTACs with Synple Automated Synthesis Platform (SYNPLE-SC002)
其他說明
Targeted Protein Degradation by Small Molecules
Destruction of DNA-Binding Proteins by Programmable Oligonucleotide PROTAC (O′PROTAC): Effective Targeting of LEF1 and ERG
Small-Molecule PROTACS: New Approaches to Protein Degradation
Targeted Protein Degradation: from Chemical Biology to Drug Discovery
Impact of linker length on the activity of PROTACs
Destruction of DNA-Binding Proteins by Programmable Oligonucleotide PROTAC (O′PROTAC): Effective Targeting of LEF1 and ERG
Small-Molecule PROTACS: New Approaches to Protein Degradation
Targeted Protein Degradation: from Chemical Biology to Drug Discovery
Impact of linker length on the activity of PROTACs
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Daniel P Bondeson et al.
Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 57, 107-123 (2016-10-13)
Protein homeostasis networks are highly regulated systems responsible for maintaining the health and productivity of cells. Whereas therapeutics have been developed to disrupt protein homeostasis, more recently identified techniques have been used to repurpose homeostatic networks to effect degradation of
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務